Intramuscular Pulsed Radiofrequency Upregulates BNDF-TrKB Expression in the Spinal Cord in Rats as an Alternative Treatment for Complicated Pain
- PMID: 39000303
- PMCID: PMC11240886
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137199
Intramuscular Pulsed Radiofrequency Upregulates BNDF-TrKB Expression in the Spinal Cord in Rats as an Alternative Treatment for Complicated Pain
Abstract
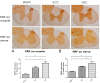
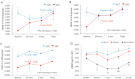
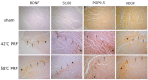
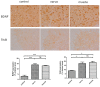
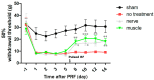
Two cases of complicated pain exist: posterior screw fixation and myofascial pain. Intramuscular pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) may be an alternative treatment for such patients. This is a two-stage animal study. In the first stage, two muscle groups and two nerve groups were subdivided into a high-temperature group with PRF at 58 °C and a regular temperature with PRF at 42 °C in rats. In the second stage, two nerve injury groups were subdivided into nerve injury with PRF 42 °C on the sciatic nerve and muscle. Blood and spinal cord samples were collected. In the first stage, the immunohistochemical analysis showed that PRF upregulated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the spinal cord in both groups of rats. In the second stage, the immunohistochemical analysis showed significant BDNF and tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) expression within the spinal cord after PRF in muscles and nerves after nerve injury. The blood biomarkers showed a significant increase in BDNF levels. PRF in the muscle in rats could upregulate BDNF-TrkB in the spinal cord, similar to PRF on the sciatica nerve for pain relief in rats. PRF could be considered clinically for patients with complicated pain and this study also demonstrated the role of BDNF in pain modulation. The optimal temperature for PRF was 42 °C.
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; intercellular adhesion molecule 1; muscle; myofascial pain syndrome; posterior spinal instrumentation; pulsed radiofrequency treatment; tropomyosin receptor kinase B; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spinal Interferon Regulatory Factor 8 and Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Prefrontal Cortex are Involved in Pain-induced Depression Relief via Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency in a Rat Spared Nerve Injury Model.Pain Physician. 2023 Mar;26(2):187-196. Pain Physician. 2023. PMID: 36988364
-
Microglial BDNF, PI3K, and p-ERK in the Spinal Cord Are Suppressed by Pulsed Radiofrequency on Dorsal Root Ganglion to Ease SNI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats.Pain Res Manag. 2019 Apr 28;2019:5948686. doi: 10.1155/2019/5948686. eCollection 2019. Pain Res Manag. 2019. PMID: 31182984 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed Radiofrequency Reduced Neuropathic Pain Behavior in Rats Associated with Upregulation of GDNF Expression.Pain Physician. 2016 Feb;19(2):49-58. Pain Physician. 2016. PMID: 26815249
-
Downregulated spinal IRF8 and BDNF in NAC are involved in neuropathic pain-induced depression relief via pulsed radiofrequency on dorsal root ganglion in rat SNI model.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Mar;146:192-200. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30639279
-
Pulsed radiofrequency modulates pain regulatory gene expression along the nociceptive pathway.Pain Physician. 2013 Sep-Oct;16(5):E601-13. Pain Physician. 2013. PMID: 24077210
References
-
- Herzberg D.E., Hedie A. Bustamante animal models of chronic pain. Are naturally occurring diseases a potential model for translational research. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2021;53:47–54. doi: 10.4067/S0719-81322021000100047. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

