The Gut Microbial Regulation of Epigenetic Modification from a Metabolic Perspective
- PMID: 39000282
- PMCID: PMC11241073
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137175
The Gut Microbial Regulation of Epigenetic Modification from a Metabolic Perspective
Abstract
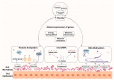
Obesity is a global health challenge that has received increasing attention in contemporary research. The gut microbiota has been implicated in the development of obesity, primarily through its involvement in regulating various host metabolic processes. Recent research suggests that epigenetic modifications may serve as crucial pathways through which the gut microbiota and its metabolites contribute to the pathogenesis of obesity and other metabolic disorders. Hence, understanding the interplay between gut microbiota and epigenetic mechanisms is crucial for elucidating the impact of obesity on the host. This review primarily focuses on the understanding of the relationship between the gut microbiota and its metabolites with epigenetic mechanisms in several obesity-related pathogenic mechanisms, including energy dysregulation, metabolic inflammation, and maternal inheritance. These findings could serve as novel therapeutic targets for probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation tools in treating metabolic disruptions. It may also aid in developing therapeutic strategies that modulate the gut microbiota, thereby regulating the metabolic characteristics of obesity.
Keywords: epigenetic modification; gut microbiota; metabolites; obesity; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications.Adv Nutr. 2019 Jan 1;10(suppl_1):S17-S30. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy078. Adv Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30721960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial dysbiosis-induced obesity: role of gut microbiota in homoeostasis of energy metabolism.Br J Nutr. 2020 May 28;123(10):1127-1137. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520000380. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Br J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32008579
-
Gut Microbiota as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Disorders.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(9):984-1001. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171009121702. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28990516 Review.
-
The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 20;13:1025706. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1025706. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36339448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microbiota-gut-brain axis in obesity.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Oct;2(10):747-756. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30147-4. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28844808 Review.
References
-
- Devajit M., Haradhan Kumar M. Obesity and Its Related Diseases: A New Escalating Alarming in Global Health. J. Innov. Med. Res. 2023;2:12–23.
-
- Chong B., Jayabaskaran J., Kong G., Chan Y.H., Chin Y.H., Goh R., Kannan S., Ng C.H., Loong S., Kueh M.T.W., et al. Trends and predictions of malnutrition and obesity in 204 countries and territories: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;57:101850. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101850. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

