Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor
- PMID: 39000047
- PMCID: PMC11241170
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136939
Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor
Abstract
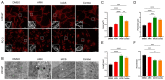
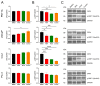
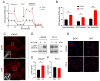
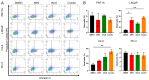
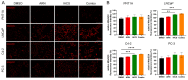
Metabolic reprogramming and mitochondrial dynamics are pivotal in prostate cancer (PCa) progression and treatment resistance, making them essential targets for therapeutic intervention. In this study, we investigated the effects of the androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide (ARN) and the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I inhibitor IACS-010759 (IACS) on the mitochondrial network architecture and dynamics in PCa cells. Treatment with ARN and/or IACS induced significant changes in mitochondrial morphology, particularly elongation, in androgen-sensitive PCa cells. Additionally, ARN and IACS modulated the mitochondrial fission and fusion processes, indicating a convergence of metabolic and androgen-signaling pathways in shaping mitochondrial function. Notably, the combination treatment with ARN and IACS resulted in increased apoptotic cell death and mitochondrial oxidative stress selectively in the androgen-sensitive PCa cells. Our findings highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial metabolism in prostate cancer and emphasize the need for further mechanistic understanding to optimize treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: IACS-010759; apalutamide; mitochondria; oxidative stress; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Metabolic Vulnerabilities to Overcome Prostate Cancer Resistance: Dual Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibition.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;15(23):5612. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235612. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067315 Free PMC article.
-
Apalutamide: the established and emerging roles in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jun;27(6):553-559. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1484107. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29856649 Review.
-
Comparison of the effect of the antiandrogen apalutamide (ARN-509) versus bicalutamide on the androgen receptor pathway in prostate cancer cell lines.Anticancer Drugs. 2018 Apr;29(4):323-333. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000592. Anticancer Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29381490
-
Phase 2 Study of the Safety and Antitumor Activity of Apalutamide (ARN-509), a Potent Androgen Receptor Antagonist, in the High-risk Nonmetastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Cohort.Eur Urol. 2016 Dec;70(6):963-970. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 May 6. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 27160947 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Apalutamide and its use in the treatment of prostate cancer.Future Oncol. 2019 Feb;15(6):591-599. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0546. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Future Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30426794 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mtPCDI: a machine learning-based prognostic model for prostate cancer recurrence.Front Genet. 2024 Sep 4;15:1430565. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1430565. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39296545 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

