To Erase or Not to Erase: Non-Canonical Catalytic Functions and Non-Catalytic Functions of Members of Histone Lysine Demethylase Families
- PMID: 39000010
- PMCID: PMC11241480
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136900
To Erase or Not to Erase: Non-Canonical Catalytic Functions and Non-Catalytic Functions of Members of Histone Lysine Demethylase Families
Abstract
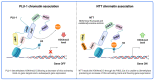
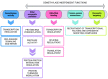
Histone lysine demethylases (KDMs) play an essential role in biological processes such as transcription regulation, RNA maturation, transposable element control, and genome damage sensing and repair. In most cases, their action requires catalytic activities, but non-catalytic functions have also been shown in some KDMs. Indeed, some strictly KDM-related proteins and some KDM isoforms do not act as histone demethylase but show other enzymatic activities or relevant non-enzymatic functions in different cell types. Moreover, many studies have reported on functions potentially supported by catalytically dead mutant KDMs. This is probably due to the versatility of the catalytical core, which can adapt to assume different molecular functions, and to the complex multi-domain structure of these proteins which encompasses functional modules for targeting histone modifications, promoting protein-protein interactions, or recognizing nucleic acid structural motifs. This rich modularity and the availability of multiple isoforms in the various classes produced variants with enzymatic functions aside from histone demethylation or variants with non-catalytical functions during the evolution. In this review we will catalog the proteins with null or questionable demethylase activity and predicted or validated inactive isoforms, summarizing what is known about their alternative functions. We will then go through some experimental evidence for the non-catalytical functions of active KDMs.
Keywords: cancer epigenetics; catalytic-independent functions; histone demethylases; histone modifications; protein isoforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessing histone demethylase inhibitors in cells: lessons learned.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017 Mar 1;10:9. doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0116-6. eCollection 2017. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017. PMID: 28265301 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting histone demethylases as a potential cancer therapy (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Sep;61(3):103. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5393. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35801593 Review.
-
Lysine Demethylation in Pathogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1433:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-38176-8_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37751133
-
The catalytic domains of all human KDM5 JmjC demethylases catalyse N-methyl arginine demethylation.FEBS Lett. 2023 Apr;597(7):933-946. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14586. Epub 2023 Feb 7. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36700827 Free PMC article.
-
Taking Me away: the function of phosphorylation on histone lysine demethylases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Mar;49(3):257-276. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.12.004. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38233282 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone methylation modification and diabetic kidney disease: Potential molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Nov;54(5):104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5428. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39301658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

