The Caenorhabditis elegans cuticle and precuticle: a model for studying dynamic apical extracellular matrices in vivo
- PMID: 38995735
- PMCID: PMC11304992
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyae072
The Caenorhabditis elegans cuticle and precuticle: a model for studying dynamic apical extracellular matrices in vivo
Abstract
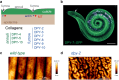
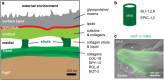
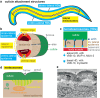
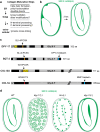
Apical extracellular matrices (aECMs) coat the exposed surfaces of animal bodies to shape tissues, influence social interactions, and protect against pathogens and other environmental challenges. In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, collagenous cuticle and zona pellucida protein-rich precuticle aECMs alternately coat external epithelia across the molt cycle and play many important roles in the worm's development, behavior, and physiology. Both these types of aECMs contain many matrix proteins related to those in vertebrates, as well as some that are nematode-specific. Extensive differences observed among tissues and life stages demonstrate that aECMs are a major feature of epithelial cell identity. In addition to forming discrete layers, some cuticle components assemble into complex substructures such as ridges, furrows, and nanoscale pillars. The epidermis and cuticle are mechanically linked, allowing the epidermis to sense cuticle damage and induce protective innate immune and stress responses. The C. elegans model, with its optical transparency, facilitates the study of aECM cell biology and structure/function relationships and all the myriad ways by which aECM can influence an organism.
Keywords: C. elegans; ZP; collagen; cuticle; extracellular matrix.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The author(s) declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans Hedgehog-related proteins are tissue- and substructure-specific components of the cuticle and precuticle.Genetics. 2024 Aug 7;227(4):iyae081. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae081. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38739761
-
Epithelial Shaping by Diverse Apical Extracellular Matrices Requires the Nidogen Domain Protein DEX-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2019 Jan;211(1):185-200. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301752. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30409789 Free PMC article.
-
Meisosomes, folded membrane microdomains between the apical extracellular matrix and epidermis.Elife. 2023 Mar 13;12:e75906. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75906. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36913486 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans Apical Extracellular Matrices Shape Epithelia.J Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 6;8(4):23. doi: 10.3390/jdb8040023. J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33036165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Form and function of the apical extracellular matrix: new insights from Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, and the vertebrate inner ear.Fac Rev. 2020 Dec 22;9:27. doi: 10.12703/r/9-27. eCollection 2020. Fac Rev. 2020. PMID: 33659959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Pax transcription factor EGL-38 links EGFR signaling to assembly of a cell-type specific apical extracellular matrix in the Caenorhabditis elegans vulva.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 6:2024.09.04.611291. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.611291. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Dev Biol. 2025 Jan;517:265-277. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.10.008 PMID: 39282387 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
In-cell processing enables rapid and in-depth proteome analysis of low-input Caenorhabditis elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.09.18.613705. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.18.613705. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345438 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis to Reveal the Impacts of Shewanella algae on the Development and Lifespan of Marine Nematode Litoditis marina.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9111. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169111. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201797 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans Hedgehog-related proteins are tissue- and substructure-specific components of the cuticle and precuticle.Genetics. 2024 Aug 7;227(4):iyae081. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae081. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38739761
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans Dispatched ortholog, CHE-14, is dispensable for apical secretion of the Hedgehog-related proteins GRL-2 and WRT-10.MicroPubl Biol. 2024 Sep 25;2024:10.17912/micropub.biology.001329. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001329. eCollection 2024. MicroPubl Biol. 2024. PMID: 39391293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abolafia J. 2006. Order Rhabditida: suborder Rhabditina. In: Eyualem-Abebe EA, Traunspurger W, Andrássy I, editors. Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy. Wallingford (UK): CAB International. p. 696–721. doi:10.1079/9780851990095.0696. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

