Epsti1 Regulates the Inflammatory Stage of Early Muscle Regeneration through STAT1-VCP Interaction
- PMID: 38993551
- PMCID: PMC11234217
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.94675
Epsti1 Regulates the Inflammatory Stage of Early Muscle Regeneration through STAT1-VCP Interaction
Abstract
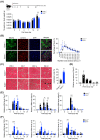
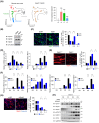
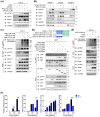
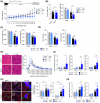
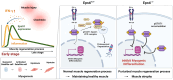
During muscle regeneration, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) coordinates inflammatory responses critical for activation of quiescent muscle stem cells upon injury via the Janus kinase (JAK) - signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) pathway. Dysregulation of JAK-STAT1 signaling results in impaired muscle regeneration, leading to muscle dysfunction or muscle atrophy. Until now, the underlying molecular mechanism of how JAK-STAT1 signaling resolves during muscle regeneration remains largely elusive. Here, we demonstrate that epithelial-stromal interaction 1 (Epsti1), an interferon response gene, has a crucial role in regulating the IFN-γ-JAK-STAT1 signaling at early stage of muscle regeneration. Epsti1-deficient mice exhibit impaired muscle regeneration with elevated inflammation response. In addition, Epsti1-deficient myoblasts display aberrant interferon responses. Epsti1 interacts with valosin-containing protein (VCP) and mediates the proteasomal degradation of IFN-γ-activated STAT1, likely contributing to dampening STAT1-mediated inflammation. In line with the notion, mice lacking Epsti1 exhibit exacerbated muscle atrophy accompanied by increased inflammatory response in cancer cachexia model. Our study suggests a crucial function of Epsti1 in the resolution of IFN-γ-JAK-STAT1 signaling through interaction with VCP which provides insights into the unexplored mechanism of crosstalk between inflammatory response and muscle regeneration.
Keywords: Epsti1; IFN-γ-JAK-STAT1 pathway; Inflammatory response; Muscle regeneration; Ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation; VCP.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate sensitizes IFN-γ-stimulated CD4+ T cells to apoptosis via alternative activation of STAT1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Dec;23(2):434-41. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25261409
-
Signal Integration of IFN-I and IFN-II With TLR4 Involves Sequential Recruitment of STAT1-Complexes and NFκB to Enhance Pro-inflammatory Transcription.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 4;10:1253. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01253. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31231385 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of the IFN-γ-STAT1 signaling pathway in a cell line model of large granular lymphocyte leukemia.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 23;13(2):e0193429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193429. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29474442 Free PMC article.
-
EGCG mitigates neurotoxicity mediated by HIV-1 proteins gp120 and Tat in the presence of IFN-gamma: role of JAK/STAT1 signaling and implications for HIV-associated dementia.Brain Res. 2006 Dec 6;1123(1):216-225. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.09.057. Epub 2006 Oct 31. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17078933 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-γ induces salivary gland epithelial cell ferroptosis in Sjogren's syndrome via JAK/STAT1-mediated inhibition of system Xc.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Aug 20;205:116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.05.027. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37286044
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

