Direct presentation of inflammation-associated self-antigens by thymic innate-like T cells induces elimination of autoreactive CD8+ thymocytes
- PMID: 38992254
- PMCID: PMC11291280
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01899-6
Direct presentation of inflammation-associated self-antigens by thymic innate-like T cells induces elimination of autoreactive CD8+ thymocytes
Abstract
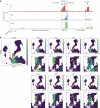
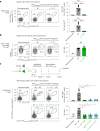
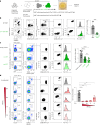
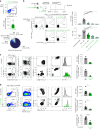
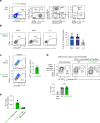
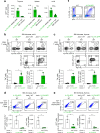
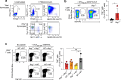
Upregulation of diverse self-antigens that constitute components of the inflammatory response overlaps spatially and temporally with the emergence of pathogen-derived foreign antigens. Therefore, discrimination between these inflammation-associated self-antigens and pathogen-derived molecules represents a unique challenge for the adaptive immune system. Here, we demonstrate that CD8+ T cell tolerance to T cell-derived inflammation-associated self-antigens is efficiently induced in the thymus and supported by redundancy in cell types expressing these molecules. In addition to thymic epithelial cells, this included thymic eosinophils and innate-like T cells, a population that expressed molecules characteristic for all major activated T cell subsets. We show that direct T cell-to-T cell antigen presentation by minute numbers of innate-like T cells was sufficient to eliminate autoreactive CD8+ thymocytes. Tolerance to such effector molecules was of critical importance, as its breach caused by decreased thymic abundance of a single model inflammation-associated self-antigen resulted in autoimmune elimination of an entire class of effector T cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Indirect presentation in the thymus limits naive and regulatory T-cell differentiation by promoting deletion of self-reactive thymocytes.Immunology. 2018 Jul;154(3):522-532. doi: 10.1111/imm.12904. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 29411880 Free PMC article.
-
The immune response to melanoma is limited by thymic selection of self-antigens.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035005. Epub 2012 Apr 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22506061 Free PMC article.
-
Self major histocompatibility complex class I antigens expressed solely in lymphoid cells do not induce tolerance in the CD4+ T cell compartment.J Exp Med. 1996 Oct 1;184(4):1573-8. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.4.1573. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8879232 Free PMC article.
-
Differential processing of self-antigens by subsets of thymic stromal cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Feb;24(1):99-104. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22296716 Review.
-
Induction of peripheral CD8+ T-cell tolerance by cross-presentation of self antigens.Immunol Rev. 1998 Oct;165:267-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01244.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9850866 Review.
References
-
- Kyewski, B. & Derbinski, J. Self-representation in the thymus: an extended view. Nat. Rev. Immunol.4, 688–698 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Anderson, M. S. et al. Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the AIRE protein. Science298, 1395–1401 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Takaba, H. et al. Fezf2 orchestrates a thymic program of self-antigen expression for immune tolerance. Cell163, 975–987 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21 1602 Pj/Cancerfonden (Swedish Cancer Society)
- PR2021-017/Barncancerfonden (Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation)
- PR2023-0091/Barncancerfonden (Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation)
- 211192/Radiumhemmets Forskningsfonder (Cancer Research Foundations of Radiumhemmet)
- 231233/Radiumhemmets Forskningsfonder (Cancer Research Foundations of Radiumhemmet)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

