Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) for Immunotherapy: Understanding Proteolysis Targeting Chimera-Driven Ubiquitin-Proteasome Interactions
- PMID: 38990186
- PMCID: PMC11342303
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.4c00253
Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) for Immunotherapy: Understanding Proteolysis Targeting Chimera-Driven Ubiquitin-Proteasome Interactions
Abstract
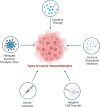
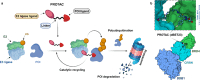
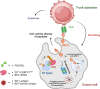
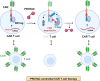
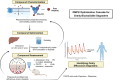
Targeted protein degradation or TPD, is rapidly emerging as a treatment that utilizes small molecules to degrade proteins that cause diseases. TPD allows for the selective removal of disease-causing proteins, including proteasome-mediated degradation, lysosome-mediated degradation, and autophagy-mediated degradation. This approach has shown great promise in preclinical studies and is now being translated to treat numerous diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, and cancer. This review discusses the latest advances in TPD and its potential as a new chemical modality for immunotherapy, with a special focus on the innovative applications and cutting-edge research of PROTACs (Proteolysis TArgeting Chimeras) and their efficient translation from scientific discovery to technological achievements. Our review also addresses the significant obstacles and potential prospects in this domain, while also offering insights into the future of TPD for immunotherapeutic applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Restraining the power of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras in the cage: A necessary and important refinement for therapeutic safety.J Cell Physiol. 2024 May;239(5):e31255. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31255. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38501341 Review.
-
The Potential of Proteolytic Chimeras as Pharmacological Tools and Therapeutic Agents.Molecules. 2020 Dec 16;25(24):5956. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245956. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33339292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redefining the Scope of Targeted Protein Degradation: Translational Opportunities in Hijacking the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway.Biochemistry. 2023 Feb 7;62(3):580-587. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00330. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Biochemistry. 2023. PMID: 34569233 Review.
-
Major advances in targeted protein degradation: PROTACs, LYTACs, and MADTACs.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100647. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100647. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33839157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Induced degradation of proteins by PROTACs and other strategies: towards promising drugs].Biol Aujourdhui. 2021;215(1-2):25-43. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2021007. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Biol Aujourdhui. 2021. PMID: 34397373 French.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

