SYT7 promotes breast cancer cells growth through the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 38988943
- PMCID: PMC11231800
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-7
SYT7 promotes breast cancer cells growth through the PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most malignant tumors in the reproductive system and has a poor prognosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the function and underlying mechanism of synaptotagmin 7 (SYT7) in breast cancer.
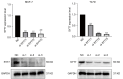
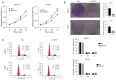
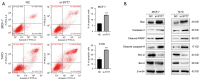
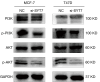
Methods: We utilized The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the Kaplan-Meier plotter database to assess the correlation between SYT7 expression and the prognosis of breast cancer patients. The efficacy of SYT7 knockdown was evaluated through reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blotting. Furthermore, we examined the impact of SYT7 on breast cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), clone formation assays, and flow cytometry. Through Western blot analysis, we investigated the influence of SYT7 on the expression of apoptosis-related markers and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in breast cancer.
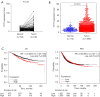
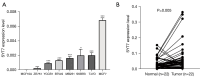
Results: The TCGA database data analysis revealed a significant up-regulation of SYT7 expression in breast cancer tissues compared to normal tissues (P<0.001). A correlation was observed between SYT7 expression and tumor size (P=0.009), as well as estrogen receptor (ER) expression level (P<0.001) and progesterone receptor (PR) expression level (P<0.001) in breast cancer patients. Analysis of the Kaplan-Meier plotter database indicated that high SYT7 expression was associated with a shorter overall survival (OS) (P=0.009). The mRNA expression results indicated higher SYT7 expression in breast cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues (P=0.005). CCK-8, clone formation assay, and flow cytometry results demonstrated that SYT7 promoted the proliferation and inhibited the apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Western blot assay confirmed the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling by SYT7.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that SYT7 is highly expressed in breast cancer and that its high expression is linked to clinical characteristics and prognosis. Inhibition of SYT7 through knockdown can suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis of breast cancer cells, making it a potential target for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT signal; Synaptotagmin 7 (SYT7); apoptosis; breast cancer; proliferation.
2024 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-7/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of tripartite motif 59 (TRIM59) inhibits proliferation in cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.044. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30822475
-
Calycosin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through down-regulation of the novel estrogen receptor-α splice variant ER-α30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154924. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154924. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37393829
-
ClpP regulates breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis by modulating the Src/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.PeerJ. 2020 Mar 10;8:e8754. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8754. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32195060 Free PMC article.
-
AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Biosci. 2021 Aug 21;11(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00677-3. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34419144 Free PMC article.
-
FOXK1 promotes malignant progression of breast cancer by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Nov;23(22):9978-9987. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201911_19564. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. Retraction in: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Mar;25(5):2159. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202103_25247 PMID: 31799667 Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
