GQIcombi application to subdue glioma via differentiation therapy
- PMID: 38988707
- PMCID: PMC11233813
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1322795
GQIcombi application to subdue glioma via differentiation therapy
Abstract
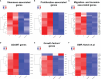
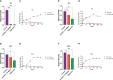
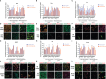
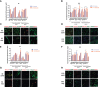
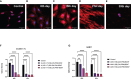
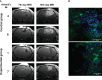
Current therapy protocols fail to cure high-grade gliomas and prevent recurrence. Therefore, novel approaches need to be developed. A re-programing of glioma cell fate is an alternative attractive way to stop tumor growth. The two-step protocol applies the antiproliferative GQ bi-(AID-1-T) and small molecule inducers with BDNF to trigger neural differentiation into terminally differentiated cells, and it is very effective on GB cell cultures. This original approach is a successful example of the "differentiation therapy". To demonstrate a versatility of this approach, in this publication we have extended a palette of cell cultures to gliomas of II, III and IV Grades, and proved an applicability of that version of differential therapy for a variety of tumor cells. We have justified a sequential mode of adding of GQIcombi components to the glioma cells. We have shown a significant retardation of tumor growth after a direct injection of GQIcombi into the tumor in rat brain, model 101/8. Thus, the proposed strategy of influencing on cancer cell growth is applicable to be further translated for therapy use.
Keywords: G-quadruplex oligonucleotides; antiproliferative activity; cancer stem cells; differentiation therapy; glioma; small molecule inducers.
Copyright © 2024 Kolesnikova, Revishchin, Fab, Alekseeva, Ryabova, Pronin, Usachev, Kopylov and Pavlova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
General commentary: GQIcombi application to subdue glioma via differentiation therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 12;14:1466102. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1466102. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39726709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Covalent Bi-Modular Parallel and Antiparallel G-Quadruplex DNA Nanocostructs Reduce Viability of Patient Glioma Primary Cell Cultures.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 25;22(7):3372. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073372. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806042 Free PMC article.
-
The Bi-(AID-1-T) G-Quadruplex Has a Janus Effect on Primary and Recurrent Gliomas: Anti-Proliferation and Pro-Migration.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 7;17(1):74. doi: 10.3390/ph17010074. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256907 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of glioma cancer stem cells in relation to histological grades in glioma specimens.Childs Nerv Syst. 2013 Feb;29(2):217-29. doi: 10.1007/s00381-012-1964-9. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013. PMID: 23143002
-
Cancer stem cells and malignant gliomas. From pathophysiology to targeted molecular therapy.J BUON. 2011 Jan-Mar;16(1):16-23. J BUON. 2011. PMID: 21674845 Review.
-
Targeted Therapeutics in Patients With High-Grade Gliomas: Past, Present, and Future.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016 Aug;17(8):42. doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0418-0. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27334978 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

