Structure of the flotillin complex in a native membrane environment
- PMID: 38985763
- PMCID: PMC11260169
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2409334121
Structure of the flotillin complex in a native membrane environment
Abstract
In this study, we used cryoelectron microscopy to determine the structures of the Flotillin protein complex, part of the Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH) superfamily, from cell-derived vesicles without detergents. It forms a right-handed helical barrel consisting of 22 pairs of Flotillin1 and Flotillin2 subunits, with a diameter of 32 nm at its wider end and 19 nm at its narrower end. Oligomerization is stabilized by the C terminus, which forms two helical layers linked by a β-strand, and coiled-coil domains that enable strong charge-charge intersubunit interactions. Flotillin interacts with membranes at both ends; through its SPFH1 domains at the wide end and the C terminus at the narrow end, facilitated by hydrophobic interactions and lipidation. The inward tilting of the SPFH domain, likely triggered by phosphorylation, suggests its role in membrane curvature induction, which could be connected to its proposed role in clathrin-independent endocytosis. The structure suggests a shared architecture across the family of SPFH proteins and will promote further research into Flotillin's roles in cell biology.
Keywords: Flotillin structure; SPFH domain; native membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
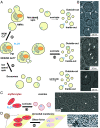
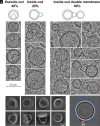
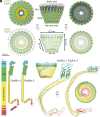
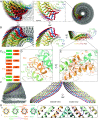


Comment in
-
Revealing the architecture of the membrane-bound Flotillin cage assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2413203121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413203121. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39162724 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The lipid raft markers stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain proteins form an operon with NfeD proteins and function with apolar polyisoprenoid lipids.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020 Feb;46(1):38-48. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2020.1716682. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31983249 Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the SPFH-NfeD family protein complex QmcA-YbbJ.Structure. 2024 Oct 3;32(10):1603-1610.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2024.07.022. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Structure. 2024. PMID: 39181124
-
¹H, ¹³C, and ¹⁵N resonance assignment of the SPFH domain of human stomatin.Biomol NMR Assign. 2012 Apr;6(1):23-5. doi: 10.1007/s12104-011-9317-2. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Biomol NMR Assign. 2012. PMID: 21643969
-
Unusual thermal disassembly of the SPFH domain oligomer from Pyrococcus horikoshii.Biophys J. 2009 Oct 7;97(7):2034-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.07.034. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19804735 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffolding microdomains and beyond: the function of reggie/flotillin proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2228-40. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5166-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16091845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the architecture of the membrane-bound Flotillin cage assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2413203121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413203121. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39162724 No abstract available.
-
An asymmetric nautilus-like HflK/C assembly controls FtsH proteolysis of membrane proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 10:2024.08.09.604662. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.09.604662. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149393 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

