STING trafficking activates MAPK-CREB signaling to trigger regulatory T cell differentiation
- PMID: 38985760
- PMCID: PMC11260101
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2320709121
STING trafficking activates MAPK-CREB signaling to trigger regulatory T cell differentiation
Abstract
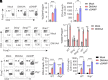
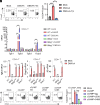
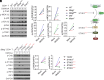
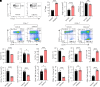
The Type-I interferon (IFN-I) response is the major outcome of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) activation in innate cells. STING is more abundantly expressed in adaptive T cells; nevertheless, its intrinsic function in T cells remains unclear. Intriguingly, we previously demonstrated that STING activation in T cells activates widespread IFN-independent activities, which stands in contrast to the well-known STING-mediated IFN response. Here, we have identified that STING activation induces regulatory T cells (Tregs) differentiation independently of IRF3 and IFN. Specifically, the translocation of STING from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity, which subsequently triggers transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) activation. The activation of the STING-MAPK-CREB signaling pathway induces the expression of many cytokine genes, including interleukin-2 (IL-2) and transforming growth factor-beta 2 (TGF-β2), to promote the Treg differentiation. Genetic knockdown of MAPK p38 or pharmacological inhibition of MAPK p38 or CREB markedly inhibits STING-mediated Treg differentiation. Administration of the STING agonist also promotes Treg differentiation in mice. In the Trex1-/- autoimmune disease mouse model, we demonstrate that intrinsic STING activation in CD4+ T cells can drive Treg differentiation, potentially counterbalancing the autoimmunity associated with Trex1 deficiency. Thus, STING-MAPK-CREB represents an IFN-independent signaling axis of STING that may have profound effects on T cell effector function and adaptive immunity.
Keywords: Innate immunity; STING; T cells; autoimmunity; type-I interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modified vaccinia virus Ankara triggers type I IFN production in murine conventional dendritic cells via a cGAS/STING-mediated cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Apr 17;10(4):e1003989. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003989. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24743339 Free PMC article.
-
TH17/Treg lymphocyte balance is regulated by beta adrenergic and cAMP signaling.Brain Behav Immun. 2025 Jan;123:1061-1070. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.11.013. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Brain Behav Immun. 2025. PMID: 39542072
-
The antiviral activity of myricetin against pseudorabies virus through regulation of the type I interferon signaling pathway.J Virol. 2024 Nov 27:e0156724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01567-24. Online ahead of print. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39601590
-
cGAS-STING pathway mediates activation of dendritic cell sensing of immunogenic tumors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Mar 21;81(1):149. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05191-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38512518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

