Transcriptome Analysis of Beta-Catenin-Related Genes in CD34+ Haematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells from Patients with AML
- PMID: 38984092
- PMCID: PMC11232677
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2024.058
Transcriptome Analysis of Beta-Catenin-Related Genes in CD34+ Haematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells from Patients with AML
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a disease of the haematopoietic stem cells(HSCs) that is characterised by the uncontrolled proliferation and impaired differentiation of normal haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Several pathways that control the proliferation and differentiation of HSCs are impaired in AML. Activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway has been shown in AML and beta-catenin, which is thought to be the key element of this pathway, has been frequently highlighted. The present study was designed to determine beta-catenin expression levels and beta-catenin-related genes in AML.
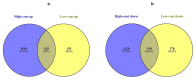
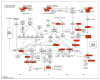
Methods: In this study, beta-catenin gene expression levels were determined in 19 AML patients and 3 controls by qRT-PCR. Transcriptome analysis was performed on AML grouped according to beta-catenin expression levels. Differentially expressed genes(DEGs) were investigated in detail using the Database for Annotation Visualisation and Integrated Discovery(DAVID), Gene Ontology(GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG), STRING online tools.
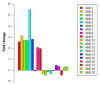
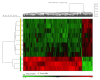
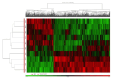
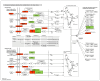
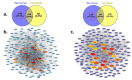
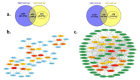
Results: The transcriptome profiles of our AML samples showed different molecular signature profiles according to their beta-catenin levels(high-low). A total of 20 genes have been identified as hub genes. Among these, TTK, HJURP, KIF14, BTF3, RPL17 and RSL1D1 were found to be associated with beta-catenin and poor survival in AML. Furthermore, for the first time in our study, the ELOV6 gene, which is the most highly up-regulated gene in human AML samples, was correlated with a poor prognosis via high beta-catenin levels.
Conclusion: It is suggested that the identification of beta-catenin-related gene profiles in AML may help to select new therapeutic targets for the treatment of AML.
Keywords: AML; Beta-catenin; CD34+ cells; DEGs; Microarray.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflict of Interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of non-classical Wnt signaling pathway effectively enhances HLA-A presentation in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 19;14:1336106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1336106. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38962268 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-29b/Sp1/FUT4 axis modulates the malignancy of leukemia stem cells by regulating fucosylation via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in acute myeloid leukemia.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 16;38(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1179-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31097000 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the key genes and microRNAs in adult acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 mutation by bioinformatics analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2020 May 18;17(9):1269-1280. doi: 10.7150/ijms.46441. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32547322 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies Key Genes and Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Associated with DNMT3A Mutation.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 23;2020:9321630. doi: 10.1155/2020/9321630. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33299888 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Role of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Through Integrated Analyses and in vivo Experiments in Vitiligo.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Sep 1;14:1089-1103. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S319061. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34511958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shipley JL, Butera JN. Acute myelogenous leukemia. Exp Hematol. 2009;37:649–658. https://doi.org:10.1016/j.exphem.2009.04.002 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ilyas M. Wnt signalling and the mechanistic basis of tumour development. J Pathol. 2005;205:130–144. https://doi.org:10.1002/path.1692 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frenquelli M, Tonon G. WNT Signaling in Hematological Malignancies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:615190. https://doi.org:10.3389/fonc.2020.615190 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayat R, Manzoor M, Hussain A. Wnt signaling pathway: A comprehensive review. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46:863–877. https://doi.org:10.1002/cbin.11797 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li XX, et al. Overexpression of CTNNB1: Clinical implication in Chinese de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214:361–367. https://doi.org:10.1016/j.prp.2018.01.003 . - DOI - PubMed

