Alternative ergosterol biosynthetic pathways confer antifungal drug resistance in the human pathogens within the Mucor species complex
- PMID: 38980037
- PMCID: PMC11323496
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01661-24
Alternative ergosterol biosynthetic pathways confer antifungal drug resistance in the human pathogens within the Mucor species complex
Abstract
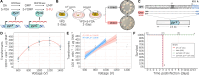
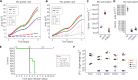
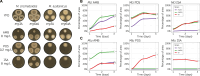
Mucormycoses are emerging fungal infections caused by a variety of heterogeneous species within the Mucorales order. Among the Mucor species complex, Mucor circinelloides is the most frequently isolated pathogen in mucormycosis patients and despite its clinical significance, there is an absence of established genome manipulation techniques to conduct molecular pathogenesis studies. In this study, we generated a spontaneous uracil auxotrophic strain and developed a genetic transformation procedure to analyze molecular mechanisms conferring antifungal drug resistance. With this new model, phenotypic analyses of gene deletion mutants were conducted to define Erg3 and Erg6a as key biosynthetic enzymes in the M. circinelloides ergosterol pathway. Erg3 is a C-5 sterol desaturase involved in growth, sporulation, virulence, and azole susceptibility. In other fungal pathogens, erg3 mutations confer azole resistance because Erg3 catalyzes the production of a toxic diol upon azole exposure. Surprisingly, M. circinelloides produces only trace amounts of this toxic diol and yet, it is still susceptible to posaconazole and isavuconazole due to alterations in membrane sterol composition. These alterations are severely aggravated by erg3Δ mutations, resulting in ergosterol depletion and, consequently, hypersusceptibility to azoles. We also identified Erg6a as the main C-24 sterol methyltransferase, whose activity may be partially rescued by the paralogs Erg6b and Erg6c. Loss of Erg6a function diverts ergosterol synthesis to the production of cholesta-type sterols, resulting in resistance to amphotericin B. Our findings suggest that mutations or epimutations causing loss of Erg6 function may arise during human infections, resulting in antifungal drug resistance to first-line treatments against mucormycosis.
Importance: The Mucor species complex comprises a variety of opportunistic pathogens known to cause mucormycosis, a potentially lethal fungal infection with limited therapeutic options. The only effective first-line treatments against mucormycosis consist of liposomal formulations of amphotericin B and the triazoles posaconazole and isavuconazole, all of which target components within the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway. This study uncovered M. circinelloides Erg3 and Erg6a as key enzymes to produce ergosterol, a vital constituent of fungal membranes. Absence of any of those enzymes leads to decreased ergosterol and consequently, resistance to ergosterol-binding polyenes such as amphotericin B. Particularly, losing Erg6a function poses a higher threat as the ergosterol pathway is channeled into alternative sterols similar to cholesterol, which maintain membrane permeability. As a result, erg6a mutants survive within the host and disseminate the infection, indicating that Erg6a deficiency may arise during human infections and confer resistance to the most effective treatment against mucormycoses.
Keywords: Erg3; Erg6; Mucorales; antifungal resistance; ergosterol; fungi; genetic tranformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Update of
-
Alternative ergosterol biosynthetic pathways confer antifungal drug resistance in the human pathogens within the Mucor species complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 1:2023.12.01.569667. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.01.569667. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0166124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01661-24. PMID: 38076934 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Alternative ergosterol biosynthetic pathways confer antifungal drug resistance in the human pathogens within the Mucor species complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 1:2023.12.01.569667. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.01.569667. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0166124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01661-24. PMID: 38076934 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Characterization of the Sterol 24-C-Methyltransferase Genes Reveals a Network of Alternative Sterol Biosynthetic Pathways in Mucor lusitanicus.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0031523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00315-23. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37036336 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of ERG3 mutations and expression of ergosterol genes controlled by UPC2 and NDT80 in Candida parapsilosis azole resistance.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017 Aug;23(8):575.e1-575.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Feb 11. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017. PMID: 28196695
-
Breaking the Mold: A Review of Mucormycosis and Current Pharmacological Treatment Options.Ann Pharmacother. 2016 Sep;50(9):747-57. doi: 10.1177/1060028016655425. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Ann Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27307416 Review.
-
Isavuconazole: A new broad-spectrum azole. Part 1: In vitro activity.J Mycol Med. 2018 Mar;28(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Mar 11. J Mycol Med. 2018. PMID: 29534853 Review.
Cited by
-
Sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51) activity in Leishmania donovani is likely dependent upon cytochrome P450 reductase 1.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 11;20(7):e1012382. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012382. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38991025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cornely OA, Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Arenz D, Chen SCA, Dannaoui E, Hochhegger B, Hoenigl M, Jensen HE, Lagrou K, Lewis RE, et al. . 2019. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of mucormycosis: an initiative of the European confederation of medical mycology in cooperation with the mycoses study group education and research consortium. Lancet Infect Dis 19:e405–e421. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30312-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoenigl M, Seidel D, Carvalho A, Rudramurthy SM, Arastehfar A, Gangneux J-P, Nasir N, Bonifaz A, Araiza J, Klimko N, Serris A, Lagrou K, Meis JF, Cornely OA, Perfect JR, White PL, Chakrabarti A, ECMM and ISHAM collaborators . 2022. The emergence of COVID-19 associated mucormycosis: a review of cases from 18 countries. Lancet Microbe 3:e543–e552. doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00237-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . 2022. WHO fungal priority pathogens list to guide research, development and public health action. Geneva.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

