Long-term severe hypoxia adaptation induces non-canonical EMT and a novel Wilms Tumor 1 (WT1) isoform
- PMID: 38977895
- PMCID: PMC11327107
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-024-00795-3
Long-term severe hypoxia adaptation induces non-canonical EMT and a novel Wilms Tumor 1 (WT1) isoform
Abstract
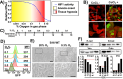
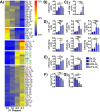
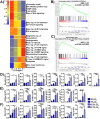
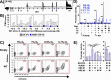
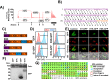
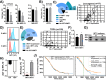
The majority of cancer deaths are caused by solid tumors, where the four most prevalent cancers (breast, lung, colorectal and prostate) account for more than 60% of all cases (1). Tumor cell heterogeneity driven by variable cancer microenvironments, such as hypoxia, is a key determinant of therapeutic outcome. We developed a novel culture protocol, termed the Long-Term Hypoxia (LTHY) time course, to recapitulate the gradual development of severe hypoxia seen in vivo to mimic conditions observed in primary tumors. Cells subjected to LTHY underwent a non-canonical epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) based on miRNA and mRNA signatures as well as displayed EMT-like morphological changes. Concomitant to this, we report production of a novel truncated isoform of WT1 transcription factor (tWt1), a non-canonical EMT driver, with expression driven by a yet undescribed intronic promoter through hypoxia-responsive elements (HREs). We further demonstrated that tWt1 initiates translation from an intron-derived start codon, retains proper subcellular localization and DNA binding. A similar tWt1 is also expressed in LTHY-cultured human cancer cell lines as well as primary cancers and predicts long-term patient survival. Our study not only demonstrates the importance of culture conditions that better mimic those observed in primary cancers, especially with regards to hypoxia, but also identifies a novel isoform of WT1 which correlates with poor long-term survival in ovarian cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wilms' tumor gene WT1 17AA(-)/KTS(-) isoform induces morphological changes and promotes cell migration and invasion in vitro.Cancer Sci. 2006 Apr;97(4):259-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00169.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16630117 Free PMC article.
-
WT1 expression in breast cancer disrupts the epithelial/mesenchymal balance of tumour cells and correlates with the metabolic response to docetaxel.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;7:45255. doi: 10.1038/srep45255. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28345629 Free PMC article.
-
Wilms' tumor protein induces an epithelial-mesenchymal hybrid differentiation state in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 15;9(7):e102041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102041. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25025131 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2020 Sep 1;487:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 26. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32470488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WT1 Alternative Splicing: Role of Its Isoforms in Neuroblastoma.J Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jun;62(2):131-141. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-0930-0. Epub 2017 May 22. J Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28534317 Review.
References
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory, International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. World Bank High Income Population Cancer Fact Sheet [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jun 27]. Available from https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/986-high-income-fa....
-
- Ritchie H, Spooner F, Roser M Causes of Death. 2018 [cited 2023 Jun 27]. Causes of death. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/causes-of-death.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

