Acute activation of hemichannels by ethanol leads to Ca2+-dependent gliotransmitter release in astrocytes
- PMID: 38974144
- PMCID: PMC11224458
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1422978
Acute activation of hemichannels by ethanol leads to Ca2+-dependent gliotransmitter release in astrocytes
Abstract
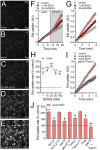
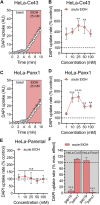
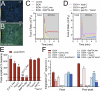
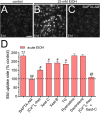
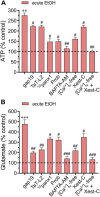
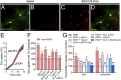
Multiple studies have demonstrated that acute ethanol consumption alters brain function and cognition. Nevertheless, the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain poorly understood. Astrocyte-mediated gliotransmission is crucial for hippocampal plasticity, and recently, the opening of hemichannels has been found to play a relevant role in this process. Hemichannels are plasma membrane channels composed of six connexins or seven pannexins, respectively, that oligomerize around a central pore. They serve as ionic and molecular exchange conduits between the cytoplasm and extracellular milieu, allowing the release of various paracrine substances, such as ATP, D-serine, and glutamate, and the entry of ions and other substances, such as Ca2+ and glucose. The persistent and exacerbated opening of hemichannels has been associated with the pathogenesis and progression of several brain diseases for at least three mechanisms. The uncontrolled activity of these channels could favor the collapse of ionic gradients and osmotic balance, the release of toxic levels of ATP or glutamate, cell swelling and plasma membrane breakdown and intracellular Ca2+ overload. Here, we evaluated whether acute ethanol exposure affects the activity of astrocyte hemichannels and the possible repercussions of this phenomenon on cytoplasmatic Ca2+ signaling and gliotransmitter release. Acute ethanol exposure triggered the rapid activation of connexin43 and pannexin1 hemichannels in astrocytes, as measured by time-lapse recordings of ethidium uptake. This heightened activity derived from a rapid rise in [Ca2+]i linked to extracellular Ca2+ influx and IP3-evoked Ca2+ release from intracellular Ca2+ stores. Relevantly, the acute ethanol-induced activation of hemichannels contributed to a persistent secondary increase in [Ca2+]i. The [Ca2+]i-dependent activation of hemichannels elicited by ethanol caused the increased release of ATP and glutamate in astroglial cultures and brain slices. Our findings offer fresh perspectives on the potential mechanisms behind acute alcohol-induced brain abnormalities and propose targeting connexin43 and pannexin1 hemichannels in astrocytes as a promising avenue to prevent deleterious consequences of alcohol consumption.
Keywords: alcoholism; connexin 43; connexins; glia; hemichannels; pannexin-1; pannexins.
Copyright © 2024 Gómez, García-Rodríguez, Marillán, Vergara, Alvear, Farias-Pasten, Sáez, Retamal, Rovegno, Ortiz and Orellana.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cx43 hemichannels and panx1 channels contribute to ethanol-induced astrocyte dysfunction and damage.Biol Res. 2024 Apr 4;57(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00493-2. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38576018 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Alcohol Exposure Activates Astroglial Hemichannels and Pannexons in the Hippocampus of Adolescent Rats: Effects on Neuroinflammation and Astrocyte Arborization.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Dec 4;12:472. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00472. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30564103 Free PMC article.
-
Hemichannels contribute to mitochondrial Ca2+ and morphology alterations evoked by ethanol in astrocytes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 26;12:1434381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1434381. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39129788 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin and pannexin hemichannels in inflammatory responses of glia and neurons.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.042. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22975435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemichannels: new pathways for gliotransmitter release.Neuroscience. 2015 Feb 12;286:45-59. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.048. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25475761 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of astrocytes in depression, its prevention, and treatment by targeting astroglial gliotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2307953121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307953121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495924
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

