The C-terminal proline-rich repeats of Enteropathogenic E. coli effector EspF are sufficient for the depletion of tight junction membrane proteins and interactions with early and recycling endosomes
- PMID: 38972985
- PMCID: PMC11229284
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-024-00626-8
The C-terminal proline-rich repeats of Enteropathogenic E. coli effector EspF are sufficient for the depletion of tight junction membrane proteins and interactions with early and recycling endosomes
Abstract
Background: Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) causes acute infantile diarrhea accounting for significant morbidity and mortality in developing countries. EPEC uses a type three secretion system to translocate more than twenty effectors into the host intestinal cells. At least four of these effectors, namely EspF, Map, EspG1/G2 and NleA, are reported to disrupt the intestinal tight junction barrier. We have reported earlier that the expression of EspF and Map in MDCK cells causes the depletion of the TJ membrane proteins and compromises the integrity of the intestinal barrier. In the present study, we have examined the role of the proline-rich repeats (PRRs) within the C-terminus of EspF in the depletion of the tight junction membrane proteins and identified key endocytosis markers that interact with EspF via these repeats.
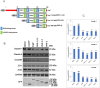
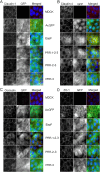
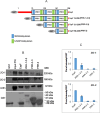
Results: We generated mutant EspF proteins which lacked one or more proline-rich repeats (PRRs) from the N-terminus of EspF and examined the effect of their expression on the cellular localization of tight junction membrane proteins. In lysates derived from cells expressing the mutant EspF proteins, we found that the C-terminal PRRs of EspF are sufficient to cause the depletion of TJ membrane proteins. Pull-down assays revealed that the PRRs mediate interactions with the TJ adaptor proteins ZO-1 and ZO-2 as well as with the proteins involved in endocytosis such as caveolin-1, Rab5A and Rab11.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the direct role of the proline-rich repeats of EspF in the depletion of the TJ membrane proteins and a possible involvement of the PRRs in the endocytosis of host proteins. New therapeutic strategies can target these PRR domains to prevent intestinal barrier dysfunction in EPEC infections.
Keywords: Endocytosis; Enteropathogenic E. Coli; EspF; Intestinal barrier; Proline rich repeats; Tight Junctions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enteropathogenic E. coli effector Map interacts with Rab13 and regulates the depletion of the tight junction proteins occludin and claudins via cathepsin B-mediated mechanisms.Biol Open. 2025 Feb 15;14(2):BIO061794. doi: 10.1242/bio.061794. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Biol Open. 2025. PMID: 39912222
-
Enteropathogenic E. coli effectors EspF and Map independently disrupt tight junctions through distinct mechanisms involving transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 27;8(1):3719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22017-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29487356 Free PMC article.
-
EPEC effector EspF promotes Crumbs3 endocytosis and disrupts epithelial cell polarity.Cell Microbiol. 2017 Nov;19(11):10.1111/cmi.12757. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12757. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Cell Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28618099 Free PMC article.
-
Tight Junction Disruption Induced by Type 3 Secretion System Effectors Injected by Enteropathogenic and Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Aug 24;6:87. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00087. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27606286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clever Cooperation: Interactions Between EspF and Host Proteins.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 22;9:2831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02831. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30524410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

