The impact of augmenter of liver regeneration in blunt liver trauma: An experimental model analysis
- PMID: 38967532
- PMCID: PMC11331352
- DOI: 10.14744/tjtes.2024.92575
The impact of augmenter of liver regeneration in blunt liver trauma: An experimental model analysis
Abstract
Background: Traumatic liver injury is an acute event that triggers liver repair. The augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) has been identified as a growth factor involved in this process. This study evaluates the impact of ALR on isolated liver blunt trauma and examines its relationship with various time intervals.
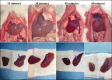
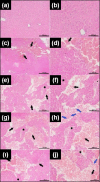
Methods: Forty healthy female Wistar albino rats were divided into five groups (n=8 each). Isolated blunt liver trauma was induced using a custom-designed trauma platform in all groups except for Group 1. The groups were categorized by the timing of euthanasia post-trauma: 2nd (15 minutes), 3rd (30 minutes), 4th (45 minutes), and 5th (60 minutes). Assessments included plasma ALR levels, liver tissue ALR levels (both intact and lacerated), biochemical indices, and liver histological analysis.
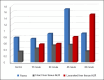
Results: Plasma ALR levels in Group 4 were higher than in Groups 1 and 2 (p<0.01). Intact liver ALR levels in Groups 3 and 4 exceeded those in Group 1 (p<0.05, p<0.01, respectively). Intact liver tissue ALR levels in Group 5 were lower than in Groups 3 and 4 (p<0.05, p<0.01, respectively). Lacerated liver tissue ALR levels in Group 5 were higher than those in Groups 2 and 3. In Group 1, the plasma ALR level was higher than the intact liver tissue ALR level (p<0.05). In Group 2, plasma ALR levels exceeded those in intact liver tissue ALR levels (p<0.01). In Group 3, plasma ALR levels surpassed both lacerated and intact liver tissue ALR levels (p<0.05, p<0.001, respectively). In Group 4, the plasma ALR level was higher than the intact liver tissue ALR level (p<0.01), and the lacerated liver tissue level was higher than the intact liver ALR level (p<0.001). Additionally, inflammation scores were higher in Groups 3, 4, and 5 compared to Group 2 (p<0.05, p<0.01, p<0.01, respectively).
Conclusion: This study is the first to explore the role of ALR in isolated blunt liver trauma. Following blunt liver trauma, both plasma and liver tissue ALR levels change within minutes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of augmenter of liver regeneration on testicular ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injury: An experimental study.Niger J Clin Pract. 2023 Jul;26(7):963-972. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_700_22. Niger J Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 37635581
-
[Augmenter of liver regeneration promotes the proliferation of HL-7702 cells in carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury via increasing autophagy].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Oct 20;24(10):761-766. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.10.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27938562 Chinese.
-
[The protective effect of augmenter of liver regeneration on mice with acute liver injury by up-regulating the expression levels of regulatory T cells].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Jan;31(1):1-5. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25575048 Chinese.
-
Augmenter of liver regeneration: Mitochondrial function and steatohepatitis.J Hepatol. 2022 Nov;77(5):1410-1421. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.019. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35777586 Review.
-
Insights on augmenter of liver regeneration cloning and function.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 21;12(31):4951-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i31.4951. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16937489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
