Biomimetic Metal-Organic Framework Gated Nanoplatform for Sonodynamic Therapy against Extensively Drug Resistant Bacterial Lung Infection
- PMID: 38962911
- PMCID: PMC11434100
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202402473
Biomimetic Metal-Organic Framework Gated Nanoplatform for Sonodynamic Therapy against Extensively Drug Resistant Bacterial Lung Infection
Abstract
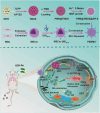
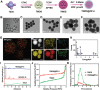
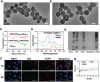
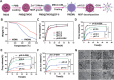
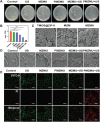
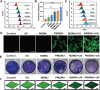
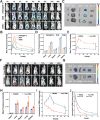
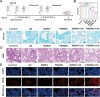
Novel antimicrobial strategies are urgently needed to treat extensively drug-resistant (XDR) bacterial infections due to the high mortality rate and lack of effective therapeutic agents. Herein, nanoengineered human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs), named PMZMU, are designed as a sonosensitizer for synergistic sonodynamic-nano-antimicrobial therapy against gram-negative XDR bacteria. PMZMU is composed of a bacterial targeting peptide (UBI29-41) modified hUC-MSCs membrane (MSCm), a sonosensitizer meso-tetra(4-car-boxyphenyl) porphine doped mesoporous organo-silica nanoparticle and an acidity-responsive metal-organic framework ZIF-8. This innovative formulation enables efficient loading of polymyxin B, reduces off-target drug release, increases circulation and targeting efficacy, and generates reactive oxygen species upon ultrasound irradiation. PMZMU exhibits remarkable in vitro inhibitory activity against four XDR bacteria: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA), and Escherichia coli. Taking advantage of the bacterial targeting ability of UBI29-41 and the inflammatory chemotaxis of hUC-MSC, PMZMU can be precisely delivered to lung infection sites thereby augmenting polymyxin B concentration. PMZMU-mediated sonodynamic therapy significantly reduces bacterial burden, relieves inflammatory damage by promoting the polarization of macrophages toward M2 phenotype, and improves survival rates without introducing adverse events. Overall, this study offers promising strategies for treating deep-tissue XDR bacterial infections, and guides the design and optimization of biomimetic nanomedicine.
Keywords: biomimetic nanoplatform; extensively drug resistant bacteria; mesenchymal stem cells; metal–organic framework; polymyxin B; sonodynamic therapy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-Switchable Nanozyme Augments Sonodynamic Therapy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infection.ACS Nano. 2020 Feb 25;14(2):2063-2076. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b08667. Epub 2020 Feb 7. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32022535
-
From Breast Cancer to Antimicrobial: Combating Extremely Resistant Gram-Negative "Superbugs" Using Novel Combinations of Polymyxin B with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators.Microb Drug Resist. 2017 Jul;23(5):640-650. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2016.0196. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Microb Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 27935770
-
Oxygen-carrying biomimetic nanoplatform for sonodynamic killing of bacteria and treatment of infection diseases.Ultrason Sonochem. 2022 Mar;84:105972. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.105972. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022. PMID: 35255361 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxin combination therapy for multidrug-resistant, extensively-drug resistant, and difficult-to-treat drug-resistant gram-negative infections: is it superior to polymyxin monotherapy?Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2023 Apr;21(4):387-429. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2023.2184346. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2023. PMID: 36820511 Review.
-
Sonodynamic therapy-based nanoplatforms for combating bacterial infections.Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Nov;100:106617. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106617. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023. PMID: 37769588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82070017/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82370014/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82100014/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- TGRH012/The Medical-Industrial Integration Project of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University
- BXS1-22003/Beijing Medical and Health Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
