Upregulation of TCPTP in Macrophages Is Involved in IL-35 Mediated Attenuation of Experimental Colitis
- PMID: 38962170
- PMCID: PMC11221972
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/3282679
Upregulation of TCPTP in Macrophages Is Involved in IL-35 Mediated Attenuation of Experimental Colitis
Abstract
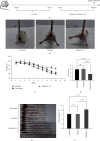
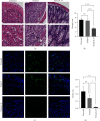
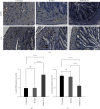
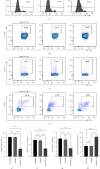
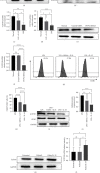
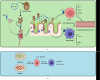
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic intestinal inflammatory disease with complex etiology. Interleukin-35 (IL-35), as a cytokine with immunomodulatory function, has been shown to have therapeutic effects on UC, but its mechanism is not yet clear. Therefore, we constructed Pichia pastoris stably expressing IL-35 which enables the cytokines to reach the diseased mucosa, and explored whether upregulation of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TCPTP) in macrophages is involved in the mechanisms of IL-35-mediated attenuation of UC. After the successful construction of engineered bacteria expressing IL-35, a colitis model was successfully induced by giving BALB/c mice a solution containing 3% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). Mice were treated with Pichia/IL-35, empty plasmid-transformed Pichia (Pichia/0), or PBS by gavage, respectively. The expression of TCPTP in macrophages (RAW264.7, BMDMs) and intestinal tissues after IL-35 treatment was detected. After administration of Pichia/IL-35, the mice showed significant improvement in weight loss, bloody stools, and shortened colon. Colon pathology also showed that the inflammatory condition of mice in the Pichia/IL-35 treatment group was alleviated. Notably, Pichia/IL-35 treatment not only increases local M2 macrophages but also decreases the expression of inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in the colon. With Pichia/IL-35 treatment, the proportion of M1 macrophages, Th17, and Th1 cells in mouse MLNs were markedly decreased, while Tregs were significantly increased. In vitro experiments, IL-35 significantly promoted the expression of TCPTP in macrophages stimulated with LPS. Similarly, the mice in the Pichia/IL-35 group also expressed more TCPTP than that of the untreated group and the Pichia/0 group.
Copyright © 2024 Baoren Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oral Escherichia coli expressing IL-35 meliorates experimental colitis in mice.J Transl Med. 2018 Mar 20;16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1441-7. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29554971 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Amauroderma rugosum on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the regulation of macrophage polarization and suppression of oxidative stress.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116901. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116901. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38878683
-
Artemisinin analogue SM934 ameliorates DSS-induced mouse ulcerative colitis via suppressing neutrophils and macrophages.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Oct;39(10):1633-1644. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.185. Epub 2018 May 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29849131 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Aggravates Mouse Experimental Colitis by Increased NFκB Activity in Macrophages.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 4;10(8):e0133598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133598. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26241646 Free PMC article.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Acute Colitis by NLRP3 Activation.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0073021. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00730-21. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34612661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamamoto-Furusho J. K., Harbi O. A., Armuzzi A., et al. Incidence of suboptimal response to tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy in inflammatory bowel disease in newly industrialised countries: the EXPLORE study. Digestive and Liver Disease . 2020;52(8):869–877. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.031. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

