Icanbelimod (CBP-307), a next-generation Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, in healthy men: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability in a randomized trial in Australia
- PMID: 38953034
- PMCID: PMC11216006
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380975
Icanbelimod (CBP-307), a next-generation Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, in healthy men: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability in a randomized trial in Australia
Abstract
Background: Icanbelimod (formerly CBP-307) is a next-generation S1PR modulator, targeting S1PR1. In this first-in-human study, icanbelimod was investigated in healthy men in Australia.
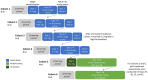
Methods: Participants were randomized 3:1, double-blind, to icanbelimod or placebo in four single-dose cohorts (0.1 mg, 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg [n=8 per cohort], 2.5 mg [n=4]) or for 28-days once-daily treatment in two cohorts (0.15 mg, 0.25 mg [n=8 per cohort]). Participants in the 0.25-mg cohort received 0.1 mg on Day 1. Treatments were administered orally after fasting; following one-week washout, icanbelimod was administered after breakfast in the 0.5-mg cohort.
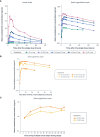
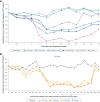
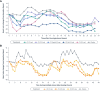
Results: Icanbelimod exposure increased rapidly and dose-dependently with single and multiple dosing (Tmax 4-7 hours). Lymphocyte counts decreased rapidly after single (-11%, 0.1 mg; -40%, 0.25 mg; -71%, 0.5 mg; -77%, 2.5 mg) and multiple doses (-49%, 0.15 mg; -75%, 0.25 mg), and recovered quickly, 7 days after dosing. After single-dose 0.5 mg, although a high-fat breakfast versus fasting did not affect maximal decrease, lymphocyte counts tended to be lower after breakfast across most timepoints up to 72 hours. Twenty-eight participants (63.6%) experienced mainly mild treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). After single-dose icanbelimod, the most common TEAEs were headache (28.6%, n=6) and dizziness (19.0%, n=4). Three participants experienced transient bradycardia, with one serious, following single-dose 2.5 mg icanbelimod. After multiple-dose icanbelimod, the most common TEAEs were headache (50.0%, n=6) and lymphopenia (41.7%, n=5), and two participants withdrew due to non-serious TEAEs. Up-titration attenuated heart rate reductions.
Conclusion: Icanbelimod was well-tolerated up to 0.5 mg and effectively reduced lymphocyte counts.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT02280434.b.
Keywords: CBP-307; Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator; icanbelimod; lymphocyte reduction; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; safety.
Copyright © 2024 Lickliter, Yang, Guo, Pan and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JL was employed by company Nucleus Network. Authors XY, JG, WP, and ZW were full-time employees of Connect Biopharma at the time of the study. The authors declare that this study received funding from Connect Biopharma. The funder was involved in the trial design.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Etrasimod: Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Studies in Healthy Adults.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024 May;13(5):534-548. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1379. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024. PMID: 38345530 Clinical Trial.
-
The safety and pharmacokinetics of a novel, selective S1P1R modulator in healthy participants.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Apr;29(4):411-422. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1742322. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32306792 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 1, randomized study to evaluate safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of GDC-3280, a potential novel anti-fibrotic small molecule, in healthy subjects.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Aug;69:102051. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.102051. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34166834 Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiodynamic Interactions between Two S1P1 Receptor Modulators in an Experimental Clinical Setting: Different Pharmacokinetic Properties as an Opportunity to Mitigate First-Dose Heart Rate Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 1;20(13):3232. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133232. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31266149 Free PMC article.
-
Results of two Phase 1, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Studies (Ascending Single-dose and Multiple-dose Studies) to Determine the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered LX9211 in Healthy Participants.Clin Ther. 2021 Jun;43(6):1029-1050. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.014. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Clin Ther. 2021. PMID: 34108079 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Pathway: New Opportunities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management.Drugs. 2024 Oct;84(10):1179-1197. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02094-5. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39322927 Review.
References
-
- Conrad N, Misra S, Verbakel JY, Verbeke G, Molenberghs G, Taylor PN, et al. . Incidence, prevalence, and co-occurrence of autoimmune disorders over time and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status: a population-based cohort study of 22 million individuals in the UK. Lancet. (2023) 401:1878–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00457-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alatab S, Sepanlou SG, Ikuta K, Vahedi H, Bisignano C, Safiri S, et al. . The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:17–30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

