Anoikis resistance regulates immune infiltration and drug sensitivity in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: insights from multi omics, single cell analysis and in vitro experiment
- PMID: 38953023
- PMCID: PMC11215044
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427475
Anoikis resistance regulates immune infiltration and drug sensitivity in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: insights from multi omics, single cell analysis and in vitro experiment
Abstract
Background: Anoikis is a form of programmed cell death essential for preventing cancer metastasis. In some solid cancer, anoikis resistance can facilitate tumor progression. However, this phenomenon is underexplored in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
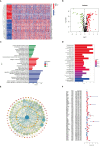
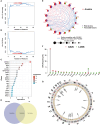
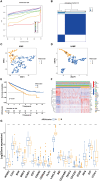
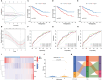
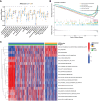
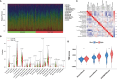
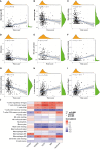
Methods: Using SVM machine learning, we identified core anoikis-related genes (ARGs) from ccRCC patient transcriptomic data. A LASSO Cox regression model stratified patients into risk groups, informing a prognostic model. GSVA and ssGSEA assessed immune infiltration, and single-cell analysis examined ARG expression across immune cells. Quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry validated ARG expression differences between immune therapy responders and non-responders in ccRCC.
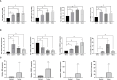
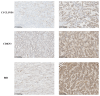
Results: ARGs such as CCND1, CDKN3, PLK1, and BID were key in predicting ccRCC outcomes, linking higher risk with increased Treg infiltration and reduced M1 macrophage presence, indicating an immunosuppressive environment facilitated by anoikis resistance. Single-cell insights showed ARG enrichment in Tregs and dendritic cells, affecting immune checkpoints. Immunohistochemical analysis reveals that ARGs protein expression is markedly elevated in ccRCC tissues responsive to immunotherapy.
Conclusion: This study establishes a novel anoikis resistance gene signature that predicts survival and immunotherapy response in ccRCC, suggesting that manipulating the immune environment through these ARGs could improve therapeutic strategies and prognostication in ccRCC.
Keywords: anoikis; immune microenvironment; prognosis; renal cell carcinoma; signature.
Copyright © 2024 Wen, Hou, Qi, Cheng, Liao, Fang, Xiao, Qiu and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Multi-Omics Identification of Interferon-γ Response Characteristics Reveals That RBCK1 Regulates the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 2;12:734646. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734646. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34795663 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering anoikis resistance and identifying prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2024 May 27;14(1):12044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62978-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38802480 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and verification of a novel anoikis-related gene signature with prognostic significance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11661-11678. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05012-6. Epub 2023 Jul 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37402968
-
Roles of the Dynamic Tumor Immune Microenvironment in the Individualized Treatment of Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 4;12:653358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653358. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of Multiparametric Evaluation of Immune-Related T-Cell Markers in Renal-Cell Carcinoma.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019 Dec;17(6):e1147-e1152. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.07.021. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31473121 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and validation of the prognostic risk model based on the anoikis-related genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2418338. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2418338. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39444152 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

