This is a preprint.
The Role of Alpha-Synuclein in Synucleinopathy: Impact on Lipid Regulation at Mitochondria-ER Membranes
- PMID: 38948777
- PMCID: PMC11212931
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.17.599406
The Role of Alpha-Synuclein in Synucleinopathy: Impact on Lipid Regulation at Mitochondria-ER Membranes
Abstract
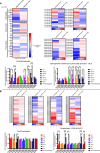
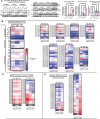
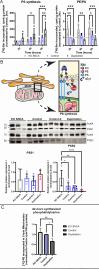
The protein alpha-synuclein (αSyn) plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of synucleinopathy, which includes Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy, and mounting evidence suggests that lipid dyshomeostasis is a critical phenotype in these neurodegenerative conditions. Previously, we identified that αSyn localizes to mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs), temporary functional domains containing proteins that regulate lipid metabolism, including the de novo synthesis of phosphatidylserine. In the present study, we have analyzed the lipid composition of postmortem human samples, focusing on the substantia nigra pars compacta of Parkinson's disease and controls, as well as three less affected brain regions of Parkinson's donors. To further assess synucleinopathy-related lipidome alterations, similar analyses were performed on the striatum of multiple system atrophy cases. Our data show region-and disease-specific changes in the levels of lipid species. Specifically, our data revealed alterations in the levels of specific phosphatidylserine species in brain areas most affected in Parkinson's disease. Some of these alterations, albeit to a lesser degree, are also observed multiples system atrophy. Using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons, we show that αSyn contributes to regulating phosphatidylserine metabolism at MAM domains, and that αSyn dosage parallels the perturbation in phosphatidylserine levels. Our results support the notion that αSyn pathophysiology is linked to the dysregulation of lipid homeostasis, which may contribute to the vulnerability of specific brain regions in synucleinopathy. These findings have significant therapeutic implications.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Parkinson’s disease; dopaminergic neuron; lipid metabolism; mitochondria-associated ER membranes; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests SP is a member of the scientific board of Luciole Pharmaceuticals and a reviewing editor for eLife.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A-Syn(ful) MAM: A Fresh Perspective on a Converging Domain in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6525. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126525. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human myeloperoxidase (hMPO) is expressed in neurons in the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease and in the hMPO-α-synuclein-A53T mouse model, correlating with increased nitration and aggregation of α-synuclein and exacerbation of motor impairment.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Sep;141:115-140. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.05.033. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31175983 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cell nigral infiltration precedes synucleinopathy in early stages of Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2020 Dec 1;143(12):3717-3733. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa269. Brain. 2020. PMID: 33118032
-
The MHC class II transactivator modulates seeded alpha-synuclein pathology and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in an in vivo rat model of Parkinson's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jan;91:369-382. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.10.017. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33223048
-
Neuropathology of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease.Neuropathology. 2022 Apr;42(2):93-103. doi: 10.1111/neup.12812. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Neuropathology. 2022. PMID: 35362115 Review.
References
-
- McCann H., Stevens C. H., Cartwright H., Halliday G. M., alpha-Synucleinopathy phenotypes. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20 Suppl 1, S62–67 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Chiba-Falek O., Lopez G. J., Nussbaum R. L., Levels of alpha-synuclein mRNA in sporadic Parkinson disease patients. Mov Disord 21, 1703–1708 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
