Understanding the structural dynamics of human islet amyloid polypeptide: Advancements in and applications of ion-mobility mass spectrometry
- PMID: 38941872
- PMCID: PMC11260546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2024.107285
Understanding the structural dynamics of human islet amyloid polypeptide: Advancements in and applications of ion-mobility mass spectrometry
Abstract
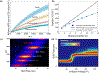
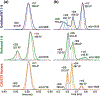
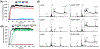
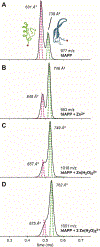
Human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) forms amyloid deposits that contribute to β-cell death in pancreatic islets and are considered a hallmark of Type II diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Evidence suggests that the early oligomers of hIAPP formed during the aggregation process are the primary pathological agent in islet amyloid induced β-cell death. The self-assembly mechanism of hIAPP, however, remains elusive, largely due to limitations in conventional biophysical techniques for probing the distribution or capturing detailed structures of the early, structurally dynamic oligomers. The advent of Ion-mobility Mass Spectrometry (IM-MS) has enabled the characterisation of hIAPP early oligomers in the gas phase, paving the way towards a deeper understanding of the oligomerisation mechanism and the correlation of structural information with the cytotoxicity of the oligomers. The sensitivity and the rapid structural characterisation provided by IM-MS also show promise in screening hIAPP inhibitors, categorising their modes of inhibition through "spectral fingerprints". This review delves into the application of IM-MS to the dissection of the complex steps of hIAPP oligomerisation, examining the inhibitory influence of metal ions, and exploring the characterisation of hetero-oligomerisation with different hIAPP variants. We highlight the potential of IM-MS as a tool for the high-throughput screening of hIAPP inhibitors, and for providing insights into their modes of action. Finally, we discuss advances afforded by recent advancements in tandem IM-MS and the combination of gas phase spectroscopy with IM-MS, which promise to deliver a more sensitive and higher-resolution structural portrait of hIAPP oligomers. Such information may help facilitate a new era of targeted therapeutic strategies for islet amyloidosis in T2DM.
Keywords: Amylin; IAPP; Ion-mobility mass spectrometry; Mass spectrometry; Protein aggregation; Type-II diabetes Mellitus.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
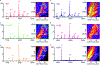
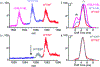
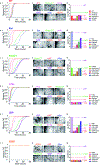
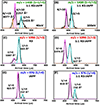
Figures
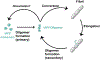
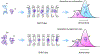

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-aggregation effect of carbon quantum dots on diabetogenic and beta-cell cytotoxic amylin and beta amyloid heterocomplexes.Nanoscale. 2022 Oct 13;14(39):14683-14694. doi: 10.1039/d2nr03173f. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 36165351
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
References
-
- Kahn SE, D’Alessio DA, Schwartz MW, Fujimoto WY, Ensinck JW, Taborsky GJ, and Porte D. 1990. Evidence of cosecretion of islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin by β-cells. Nestle. Nutr. Works. Se. 39:634–638. - PubMed
-
- Lukinius A, Wilander E, Westermark GT, Engström U, and Westermark P. 1989. Co-localization of islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin in the B cell secretory granules of the human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 32:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Stridsberg M, Sandler S, and Wilander E. 1993. Cosecretion of islet amylid polypeptide (IAPP) and insulin from isolated rat pancreatic islets following stimulation or inhibition of β-cell function. Regul. Pept. 45:363–70. - PubMed
-
- Lutz TA. 2013. The interaction of amylin with other hormones in the control of eating. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 15:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Lutz TA. 2010. The role of amylin in the control of energy homeostasis. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 298:R1475–R1484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

