Sulfated Laminarin Polysaccharides Reduce the Adhesion of Nano-COM Crystals to Renal Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- PMID: 38931471
- PMCID: PMC11206474
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060805
Sulfated Laminarin Polysaccharides Reduce the Adhesion of Nano-COM Crystals to Renal Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
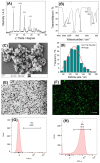
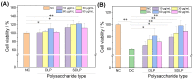
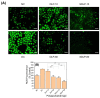
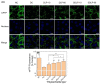
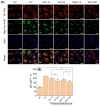
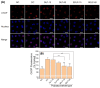
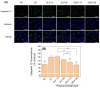
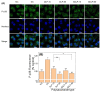
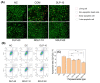
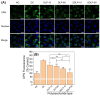
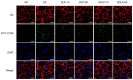
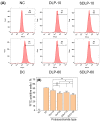
Purpose: Adhesion between calcium oxalate crystals and renal tubular epithelial cells is a vital cause of renal stone formation; however, the drugs that inhibit crystal adhesion and the mechanism of inhibition have yet to be explored. Methods: The cell injury model was constructed using nano-COM crystals, and changes in oxidative stress levels, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress levels, downstream p38 MAPK protein expression, apoptosis, adhesion protein osteopontin expression, and cell-crystal adhesion were examined in the presence of Laminarin polysaccharide (DLP) and sulfated DLP (SDLP) under protected and unprotected conditions. Results: Both DLP and SDLP inhibited nano-COM damage to human kidney proximal tubular epithelial cell (HK-2), increased cell viability, decreased ROS levels, reduced the opening of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore, markedly reduced ER Ca2+ ion concentration and adhesion molecule OPN expression, down-regulated the expression of ER stress signature proteins including CHOP, Caspase 12, and p38 MAPK, and decreased the apoptosis rate of cells. SDLP has a better protective effect on cells than DLP. Conclusions: SDLP protects HK-2 cells from nano-COM crystal-induced apoptosis by reducing oxidative and ER stress levels and their downstream factors, thereby reducing crystal-cell adhesion interactions and the risks of kidney stone formation.
Keywords: apoptosis; crystal adhesion; endoplasmic reticulum stress; sulfated polysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibition of calcium oxalate crystal formation and synergistic protection of HK-2 cells from crystal damage by sulfated Laminarin polysaccharide and potassium citrate.Biomater Sci. 2023 May 16;11(10):3524-3546. doi: 10.1039/d3bm00087g. Biomater Sci. 2023. PMID: 36995035
-
Sulfated Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharide inhibits the formation of kidney stones by inhibiting HK-2 cell damage and reducing the adhesion of nano‑calcium oxalate crystals.Biomater Adv. 2022 Mar;134:112564. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112564. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Biomater Adv. 2022. PMID: 35525730
-
Corn Silk Polysaccharide Reduces the Risk of Kidney Stone Formation by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting COM Crystal Adhesion and Aggregation.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 17;9(17):19236-19249. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00110. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38708219 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress on the damage and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells induced by calcium oxalate crystals.Urolithiasis. 2021 Aug;49(4):291-299. doi: 10.1007/s00240-021-01261-7. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Urolithiasis. 2021. PMID: 33786645
-
Corn Silk Polysaccharides with Different Carboxyl Contents Reduce the Oxidative Damage of Renal Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting Endocytosis of Nano-calcium Oxalate Crystals.ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 14;8(29):25839-25849. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01306. eCollection 2023 Jul 25. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37521646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li X., Chen S., Feng D., Fu Y., Wu H., Lu J., Bao J. Calcium-sensing receptor promotes calcium oxalate crystal adhesion and renal injury in Wistar rats by promoting ROS production and subsequent regulation of PS ectropion, OPN, KIM-1, and ERK expression. Ren. Fail. 2021;43:465–476. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1881554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

