Acute Kaempferol Stimulation Induces AKT Phosphorylation in HepG2 Cells
- PMID: 38929747
- PMCID: PMC11205056
- DOI: 10.3390/life14060764
Acute Kaempferol Stimulation Induces AKT Phosphorylation in HepG2 Cells
Abstract
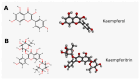
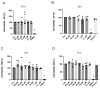
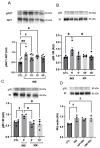
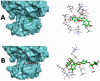
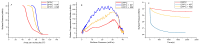
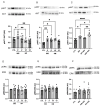
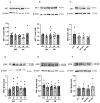
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) stands as a prevalent global public health issue caused by deficiencies in the action of insulin and/or insulin production. In the liver, insulin plays an important role by inhibiting hepatic glucose production and stimulating glycogen storage, thereby contributing to blood glucose regulation. Kaempferitrin (KP) and kaempferol (KM), flavonoids found in Bauhinia forficata, exhibit insulin-mimetic properties, showing promise in managing T2DM. In this study, we aimed to assess the potential of these compounds in modulating the insulin signaling pathway and/or glucose metabolism. Cell viability assays confirmed the non-cytotoxic nature of both compounds toward HepG2 cells at the concentrations and times evaluated. Theoretical molecular docking studies revealed that KM had the best docking pose with the IR β subunit when compared to the KP. Moreover, Langmuir monolayer evaluation indicated molecular incorporation for both KM and KP. Specifically, KM exhibited the capability to increase AKT phosphorylation, a key kinase in insulin signaling, regardless of insulin receptor (IR) activation. Notably, KM showed an additional synergistic effect with insulin in activating AKT. In conclusion, our findings suggest the potential of KM as a promising compound for stimulating AKT activation, thereby influencing energy metabolism in T2DM.
Keywords: flavonoids; insulin signaling; liver cells; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest. The graphical abstract was created with
Figures
Similar articles
-
A diarylheptanoid compound from Alpinia officinarum Hance ameliorates high glucose-induced insulin resistance by regulating PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-GSK3β signaling pathways in HepG2 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;295:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115397. Epub 2022 May 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35605918
-
Sanhuang xiexin decoction synergizes insulin/PI3K-Akt/FoxO signaling pathway to inhibit hepatic glucose production and alleviate T2DM.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;306:116162. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116162. Epub 2023 Jan 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36646159
-
Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) water extract alleviates palmitate-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 hepatocytes via the activation of IRS1/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 and GSK-3β signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Dec 15;23(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04275-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 38102588 Free PMC article.
-
Bauhinia forficata link extract attenuates insulin resistance by preserving glucose uptake in gastrocnemius muscle.Nat Prod Res. 2023 Jun;37(12):2031-2036. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2022.2113875. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Nat Prod Res. 2023. PMID: 35997243
-
Flavonoids from Enicostema littorale blume enhances glucose uptake of cells in insulin resistant human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:268-277. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.047. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28364599
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
-
- Souza B.V.C., Araújo R.S.R.M., Silva O.A., Faustino L.C., Gonçalves M.F.B., Santos M.L., Souza G.R., Rocha L.M., Cardoso M.L.S., Nunes L.C. Bauhinia forficata In Treatment Of Diabetes Mellitus: A Patent Review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018;28:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Chandramohan G. Kaempferol, a flavonoid, ameliorates hyperglycemia by attenuating the key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin–induced experimental diabetic rats. Prog. Nutr. 2020;21:65–72. doi: 10.23751/pn.v21i2-S.6329. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

