Overcoming Resistance to Temozolomide in Glioblastoma: A Scoping Review of Preclinical and Clinical Data
- PMID: 38929657
- PMCID: PMC11204771
- DOI: 10.3390/life14060673
Overcoming Resistance to Temozolomide in Glioblastoma: A Scoping Review of Preclinical and Clinical Data
Abstract
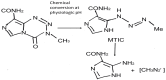
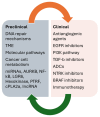
Glioblastoma (GB) is the most common and most aggressive primary brain tumor in adults, with an overall survival almost 14.6 months. Optimal resection followed by combined temozolomide chemotherapy and radiotherapy, also known as Stupp protocol, remains the standard of treatment; nevertheless, resistance to temozolomide, which can be obtained throughout many molecular pathways, is still an unsurpassed obstacle. Several factors influence the efficacy of temozolomide, including the involvement of other DNA repair systems, aberrant signaling pathways, autophagy, epigenetic modifications, microRNAs, and extracellular vesicle production. The blood-brain barrier, which serves as both a physical and biochemical obstacle, the tumor microenvironment's pro-cancerogenic and immunosuppressive nature, and tumor-specific characteristics such as volume and antigen expression, are the subject of ongoing investigation. In this review, preclinical and clinical data about temozolomide resistance acquisition and possible ways to overcome chemoresistance, or to treat gliomas without restoration of chemosensitinity, are evaluated and presented. The objective is to offer a thorough examination of the clinically significant molecular mechanisms and their intricate interrelationships, with the aim of enhancing understanding to combat resistance to TMZ more effectively.
Keywords: chemoresistance; glioblastomas; resistance mechanisms; temozolomide resistance; therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
-
Anti-angiogenic therapy for high-grade glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 22;11(11):CD008218. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008218.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480778 Free PMC article.
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines for the role of chemotherapy in newly diagnosed WHO Grade II diffuse glioma in adults: update.J Neurooncol. 2025 Jan;171(2):279-298. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04861-6. Epub 2024 Nov 20. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 39565459 Review.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Exploring conceptual and theoretical frameworks for nurse practitioner education: a scoping review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):146-55. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2150. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571290
Cited by
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Conquest in Glioblastoma Nanomedicine: Strategies, Clinical Advances, and Emerging Challenges.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;16(19):3300. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193300. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources