Trichinella spiralis Paramyosin Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Modulating CD4+ T Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 38928413
- PMCID: PMC11204176
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25126706
Trichinella spiralis Paramyosin Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Modulating CD4+ T Cell Differentiation
Abstract
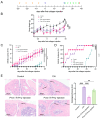
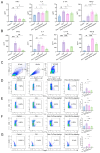
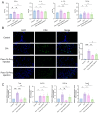
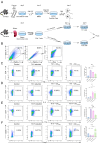
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that significantly impacts quality of life by disrupting CD4+ T cell immune homeostasis. The identification of a low-side-effect drug for RA treatment is urgently needed. Our previous study suggests that Trichinella spiralis paramyosin (Ts-Pmy) has immunomodulatory effects, but its potential effect on CD4+ T cell response in RA remains unclear. In this study, we used a murine model to investigate the role of rTs-Pmy in regulating CD4+ T cell differentiation in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Additionally, we assessed the impact of rTs-Pmy on CD4+ T cell differentiation towards the Th1 and Th17 phenotypes, which are associated with inflammatory responses in arthritis, using in vitro assays. The results demonstrated that rTs-Pmy administration reduced arthritis severity by inhibiting Th1 and Th17 response while enhancing Treg response. Prophylactic administration of Ts-Pmy showed superior efficacy on CIA compared to therapeutic administration. Furthermore, in vitro assays demonstrated that rTs-Pmy could inhibit the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th1 and Th17 while inducing the production of Tregs, suggesting a potential mechanism underlying its therapeutic effects. This study suggests that Ts-Pmy may ameliorate CIA by restoring the immune balance of CD4+ T cells and provides new insights into the mechanism through which helminth-derived proteins exert their effects on autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; T cell differentiation; Trichinella spiralis paramyosin; collagen-induced arthritis; hygiene hypothesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of a full-length cDNA encoding paramyosin of Trichinella spiralis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Jan 18;365(3):528-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.012. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18021743
-
Trichinella spiralis Infection Mitigates Collagen-Induced Arthritis via Programmed Death 1-Mediated Immunomodulation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 26;9:1566. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01566. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30093899 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of recombinant serine protease from adult stage of Trichinella spiralis on TNBS-induced experimental colitis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Sep;86:106699. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106699. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32570037
-
Identification and characterization of CD4+ T cell epitopes present in Trichinella spiralis paramyosin.Vet Parasitol. 2016 Nov 15;231:59-62. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Vet Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27353726
-
Trichinella spiralis paramyosin binds to C8 and C9 and protects the tissue-dwelling nematode from being attacked by host complement.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011 Jul;5(7):e1225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001225. Epub 2011 Jul 5. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. PMID: 21750743 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

