Plasmatic Inactive IL-18 Predicts a Worse Overall Survival for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Early Metabolic Progression after Immunotherapy Initiation
- PMID: 38927931
- PMCID: PMC11202099
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16122226
Plasmatic Inactive IL-18 Predicts a Worse Overall Survival for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Early Metabolic Progression after Immunotherapy Initiation
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the potential value of circulating active and inactive IL-18 levels in distinguishing pseudo and true tumor progression among NSCLC patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor treatments (ICIs).
Methods: This ancillary study includes 195 patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with ICI in monotherapy, either pembrolizumab or nivolumab. Plasmatic levels of IL-18-related compounds, comprising the inhibitor IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP), the inactive IL-18 (corresponding to IL-18/IL-18BP complex), and the active free IL-18, were assayed by ELISA. Objective tumoral response was analyzed by 18FDG PET-CT at baseline, 7 weeks, and 3 months post treatment induction, using PERCIST criteria.
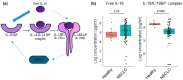
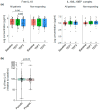
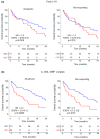
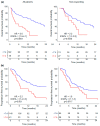
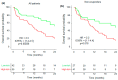
Results: Plasmatic IL-18BP and total IL-18 levels are increased at baseline in NSCLC patients compared with healthy controls, whereas IL-18/IL-18BP complexes are decreased, and free IL-18 levels remain unchanged. Neither of the IL-18-related compounds allowed to discriminate ICI responding to nonresponding patients. However, inactive IL-18 levels allowed to discriminate patients with a first tumor progression, assessed after 7 weeks of treatment, with worse overall survival. In addition, we showed that neutrophil concentration is also a predictive indicator of patients' outcomes with OS (HR = 2.6, p = 0.0001) and PFS (HR = 2.2, p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Plasmatic levels of inactive IL-18, combined with circulating neutrophil concentrations, can effectively distinguish ICI nonresponding patients with better overall survival (OS), potentially guiding rapid decisions for therapeutic intensification.
Keywords: IL-18 signaling pathways; immune checkpoint inhibitor; lung adenocarcinoma; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The utility of 68F-FDG PET/CT for evaluation of tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Hell J Nucl Med. 2021 Sep-Dec;24(3):186-198. doi: 10.1967/s002449912402. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Hell J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 34901959
-
Total metabolic tumor volume on 18F-FDG PET/CT is a game-changer for patients with metastatic lung cancer treated with immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Apr 22;12(4):e007628. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007628. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38649279 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-based treatment beyond progression with prior immunotherapy in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Jun;11(6):1027-1037. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-376. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35832458 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Feb 23;11:955-965. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S153290. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29503570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential predictive value of change in inflammatory cytokines levels subsequent to initiation of immune checkpoint inhibitor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cytokine. 2021 Feb;138:155363. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155363. Epub 2020 Nov 29. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33264749 Review.
References
-
- Araghi M., Mannani R., Heidarnejad Maleki A., Hamidi A., Rostami S., Safa S.H., Faramarzi F., Khorasani S., Alimohammadi M., Tahmasebi S., et al. Recent Advances in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeted Therapy; an Update Review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023;23:162. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02990-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mino-Kenudson M., Schalper K., Cooper W., Dacic S., Hirsch F.R., Jain D., Lopez-Rios F., Tsao M.S., Yatabe Y., Beasley M.B., et al. Predictive Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: Perspective from the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Pathology Committee. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022;17:1335–1354. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.09.109. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

