Droplet digital PCR analysis of CDH13 methylation status in Slovak women with invasive ductal breast cancer
- PMID: 38926485
- PMCID: PMC11208553
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65580-6
Droplet digital PCR analysis of CDH13 methylation status in Slovak women with invasive ductal breast cancer
Abstract
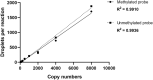
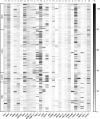
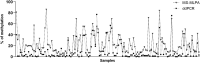
Identifying novel epigenetic biomarkers is a promising way to improve the clinical management of patients with breast cancer. Our study aimed to determine the methylation pattern of 25 tumor suppressor genes (TSG) and select the best methylation biomarker associated with clinicopathological features in the cohort of Slovak patients diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Overall, 166 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues obtained from patients with IDC were included in the study. The methylation status of the promoter regions of 25 TSG was analyzed using semiquantitative methylation-specific MLPA (MS-MLPA). We identified CDH13 as the most frequently methylated gene in our cohort of patients. Further analysis by ddPCR confirmed an increased level of methylation in the promoter region of CDH13. A significant difference in CDH13 methylation levels was observed between IDC molecular subtypes LUM A versus HER2 (P = 0.0116) and HER2 versus TNBC (P = 0.0234). In addition, significantly higher methylation was detected in HER2+ versus HER2- tumors (P = 0.0004) and PR- versus PR+ tumors (P = 0.0421). Our results provide evidence that alteration in CDH13 methylation is associated with clinicopathological features in the cohort of Slovak patients with IDC. In addition, using ddPCR as a methylation-sensitive method represents a promising approach characterized by higher precision and technical simplicity to measure the methylation of target CpGs in CDH13 compared to other conventional methods such as MS-MLPA.
Keywords: CDH13; CpG methylation; Droplet digital PCR; MS-MLPA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frequent promoter hypermethylation of BRCA2, CDH13, MSH6, PAX5, PAX6 and WT1 in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer.J Pathol. 2011 Oct;225(2):222-31. doi: 10.1002/path.2930. Epub 2011 Jun 27. J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21710692
-
CpG island methylation profile of estrogen receptor alpha in Iranian females with triple negative or non-triple negative breast cancer: new marker of poor prognosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(2):451-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.2.451. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22524805
-
Methylation profiling of ductal carcinoma in situ and its relationship to histopathological features.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Oct 21;16(5):423. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0423-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25331261 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of CDH1 in breast cancer: a meta-analysis and literature review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Sep 18;9:5277-85. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86929. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26425077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Analysis of the Relationship of CDH13 Promoter Methylation and Breast Cancer Risk and Prognosis.PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0149185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149185. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27153114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

