The diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in critically ill patients with respiratory tract infections
- PMID: 38916357
- PMCID: PMC11302328
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00458-24
The diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in critically ill patients with respiratory tract infections
Abstract
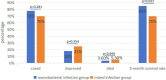
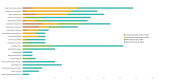
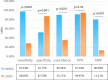
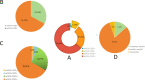
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) is an unbiased and rapid method for detecting pathogens. This study enrolled 145 suspected severe pneumonia patients who were admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University. This study primarily aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of mNGS and conventional microbiological tests (CMTs) using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples for detecting pathogens. Our findings indicated that mNGS performed significantly higher sensitivity (97.54% vs 28.68%, P < 0.001), coincidence (90.34% vs 35.17%, P < 0.001), and negative predictive value (80.00% vs 13.21%, P < 0.001) but performed lower specificity than CMTs (52.17% vs 87.5%, P < 0.001). Streptococcus pneumoniae as the most common bacterial pathogen had the largest proportion (22.90%, 30/131) in this study. In addition to bacteria, fungi, and virus, mNGS can detect a variety of atypical pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-tuberculous. Mixed infections were common in patients with severe pneumonia, and bacterial-fungal-viral-atypical pathogens were the most complicated infection. After adjustments of antibiotics based on mNGS and CMTs, the clinical manifestation improved in 139 (95.86%, 139/145) patients. Our data demonstrated that mNGS had significant advantage in diagnosing respiratory tract infections, especially atypical pathogens and fungal infections. Pathogens were detected timely and comprehensively, contributing to the adjustments of antibiotic treatments timely and accurately, improving patient prognosis and decreasing mortality potentially.IMPORTANCEMetagenomic next-generation sequencing using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid can provide more comprehensive and accurate pathogens for respiratory tract infections, especially when considering the previous usage of empirical antibiotics before admission or complicated clinical presentation. This technology is expected to play an important role in the precise application of antimicrobial drugs in the future.
Keywords: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; conventional microbiological tests; metagenomic next-generation sequencing; respiratory tract infections; severe pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing targeted and metagenomic next-generation sequencing for pulmonary infection in HIV-infected and non-HIV-infected individuals.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 19;14:1438982. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1438982. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39224706 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pediatric pneumonia.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 27;12:950531. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.950531. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36389175 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in immunocompromised patients with severe respiratory infections in the ICU.Respir Res. 2024 Oct 5;25(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02991-z. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39369191 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic next generation sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage fluids for the identification of pathogens in patients with pulmonary infection: A retrospective study.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Sep;110(1):116402. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116402. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38878340 Review.
-
The clinical application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for detecting pathogens in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: case reports and literature review.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022 May;22(5):575-582. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2022.2071607. Epub 2022 May 2. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35473493 Review.
References
-
- Langelier C, Kalantar KL, Moazed F, Wilson MR, Crawford ED, Deiss T, Belzer A, Bolourchi S, Caldera S, Fung M, et al. . 2018. Integrating host response and unbiased microbe detection for lower respiratory tract infection diagnosis in critically ill adults. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E12353–E12362. doi:10.1073/pnas.1809700115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

