Synthesis and biological research of new imidazolone-sulphonamide-pyrimidine hybrids as potential EGFR-TK inhibitors and apoptosis-inducing agents
- PMID: 38915323
- PMCID: PMC11194663
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra03157a
Synthesis and biological research of new imidazolone-sulphonamide-pyrimidine hybrids as potential EGFR-TK inhibitors and apoptosis-inducing agents
Abstract
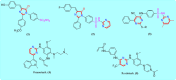
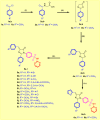
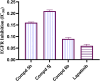
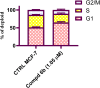
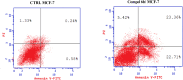
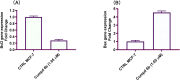
Development of new effective EGFR-targeted antitumor agents is needed because of their clinical significance. A new series of imidazolone-sulphonamide-pyrimidine hybrids was designed and synthesized as modified analogs of some reported EGFR inhibitors. The cytotoxic activity of all the synthesized hybrids was investigated against the breast MCF-7 cancerous cell line using doxorubicin (Dox) as a positive control. 4-(Furan-2-ylmethylene)imidazolone-sulphonamide-pyrimidine 6b had the best potent activity against MCF-7 cells with IC50 result of 1.05 μM, which was better than Dox (IC50 = 1.91 μM). In addition, mechanistic studies revealed the ability of compounds 5g, 5h and 6b to inhibit EGFR kinase. Cell cycle analysis revealed that compound 6b can halt MCF-7 cells at the G1 phase with a concomitant decrease in cellular percentage at the S and G2/M phases. This compound produced a noticeable rise in the proportion of apoptotic cells with regard to the untreated control. Furthermore, the effects of hybrid 6b on the expression levels of pro-apoptotic Bax and pro-survival Bcl2 were assessed. The results showed that this compound upregulated the level of Bax expression as well as declined the expression value of Bcl-2 with regard to the untreated control.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-based dual EGFR T790M/HER2 inhibitors: Design, synthesis, structure-activity relationship and biological activity as potential antitumor and anticonvulsant agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Mar 15;214:113222. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113222. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33545637
-
New thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-based derivatives: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation as antiproliferative agents, EGFR and ARO inhibitors inducing apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Oct;115:105208. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105208. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34365057
-
Novel pyrazole-based COX-2 inhibitors as potential anticancer agents: Design, synthesis, cytotoxic effect against resistant cancer cells, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction and dual EGFR/Topo-1 inhibition.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Feb;131:106273. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106273. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36444790
-
Synthesis, characterization and biological research of novel 2-(quinoline-4-carbonyl)hydrazide-acrylamide hybrids as potential anticancer agents on MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells by targeting EGFR-TK.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 26;14(32):23495-23504. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03963g. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39071480 Free PMC article.
-
New series of isoxazole derivatives targeting EGFR-TK: Synthesis, molecular modeling and antitumor evaluation.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Nov 1;28(21):115674. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115674. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33065442
References
-
- Hakkimane S. S. and Gaonkar S. L., Chapter 1–Biology of cancer: current insights and perspectives, in Treatment Landscape of Targeted Therapies in Oncology, ed. P. K. Maurya and V. Saini, Academic Press, 2023, pp. 1–11
-
- Sriharikrishnaa S., Suresh P. S. and Prasada K. S., An Introduction to Fundamentals of Cancer Biology, in Optical Polarimetric Modalities for Biomedical Research, ed. N. Mazumder, et al., Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2023, pp. 307–330
-
- Cuthrell K. M. Tzenios N. Breast Cancer: Updated and Deep Insights. Int. J. Oncol. 2023;6:104–118.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

