A Broad-specificity Neutralizing Nanobody against Hepatitis E Virus Capsid Protein
- PMID: 38905108
- PMCID: PMC11299488
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300706
A Broad-specificity Neutralizing Nanobody against Hepatitis E Virus Capsid Protein
Abstract
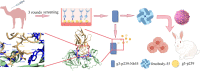
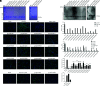
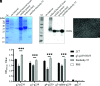
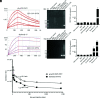
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a worldwide zoonotic and public health concern. The study of HEV biology is helpful for designing viral vaccines and drugs. Nanobodies have recently been considered appealing materials for viral biological research. In this study, a Bactrian camel was immunized with capsid proteins from different genotypes (1, 3, 4, and avian) of HEV. Then, a phage library (6.3 × 108 individual clones) was constructed using peripheral blood lymphocytes from the immunized camel, and 12 nanobodies against the truncated capsid protein of genotype 3 HEV (g3-p239) were screened. g3-p239-Nb55 can cross-react with different genotypes of HEV and block Kernow-C1/P6 HEV from infecting HepG2/C3A cells. To our knowledge, the epitope recognized by g3-p239-Nb55 was determined to be a novel conformational epitope located on the surface of viral particles and highly conserved among different mammalian HEV isolates. Next, to increase the affinity and half-life of the nanobody, it was displayed on the surface of ferritin, which can self-assemble into a 24-subunit nanocage, namely, fenobody-55. The affinities of fenobody-55 to g3-p239 were ∼20 times greater than those of g3-p239-Nb55. In addition, the half-life of fenobody-55 was nine times greater than that of g3-p239-Nb55. G3-p239-Nb55 and fenobody-55 can block p239 attachment and Kernow-C1/P6 infection of HepG2/C3A cells. Fenobody-55 can completely neutralize HEV infection in rabbits when it is preincubated with nonenveloped HEV particles. Our study reported a case in which a nanobody neutralized HEV infection by preincubation, identified a (to our knowledge) novel and conserved conformational epitope of HEV, and provided new material for researching HEV biology.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

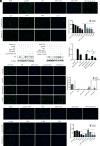
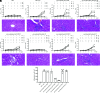

Similar articles
-
Characterization of Three Novel Linear Neutralizing B-Cell Epitopes in the Capsid Protein of Swine Hepatitis E Virus.J Virol. 2018 Jun 13;92(13):e00251-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00251-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29669835 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal investigation of rat hepatitis E virus antigenicity: Implications for infection, diagnostics, and vaccine efficacy.J Hepatol. 2021 Jun;74(6):1315-1324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.028. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33845058
-
Characterization of Two Novel Linear B-Cell Epitopes in the Capsid Protein of Avian Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) That Are Common to Avian, Swine, and Human HEVs.J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5491-501. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00107-15. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25741007 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis E virus: neutralizing sites, diagnosis, and protective immunity.Rev Med Virol. 2012 Sep;22(5):339-49. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1719. Epub 2012 May 30. Rev Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 22645002 Review.
-
Hepatitis E Virus Genotypes and Evolution: Emergence of Camel Hepatitis E Variants.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 20;18(4):869. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040869. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28425927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pillot, J., Türkoglu S., Dubreuil P., Cosson A., Lemaigre G., Meng J., Lazizi Y.. 1995. Cross-reactive immunity against different strains of the hepatitis E virus transferable by simian and human sera. C. R. Acad. Sci III 318: 1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Smith., D. B., Simmonds P.; Members of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses Study Group ; Jameel S., Emerson S. U., Harrison T. J., Meng X.-J., Okamoto H., Van der Poel W. H. M., and Purdy M. A.. 2014. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 95: 2223–2232. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Purdy, M. A., Drexler J. F., Meng X.-J., Norder H., Okamoto H., Van der Poel W. H. M., Reuter G., de Souza W. M., Ulrich R. G., Smith D. B.. 2022. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol 103: jgv.0.001778. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31972676/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2022JC-12/陕西省科学技术厅 | Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation)
- 2023YFD1800304/MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China (NKPs)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

