This is a preprint.
CLCC1 promotes hepatic neutral lipid flux and nuclear pore complex assembly
- PMID: 38895340
- PMCID: PMC11185754
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.07.597858
CLCC1 promotes hepatic neutral lipid flux and nuclear pore complex assembly
Abstract
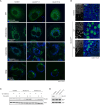
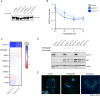
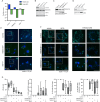
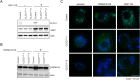
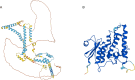
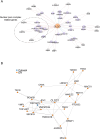
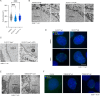
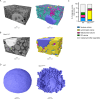
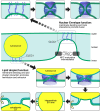
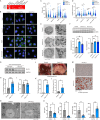
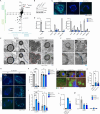
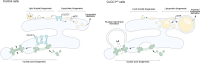
Imbalances in lipid storage and secretion lead to the accumulation of hepatocyte lipid droplets (LDs) (i.e., hepatic steatosis). Our understanding of the mechanisms that govern the channeling of hepatocyte neutral lipids towards cytosolic LDs or secreted lipoproteins remains incomplete. Here, we performed a series of CRISPR-Cas9 screens under different metabolic states to uncover mechanisms of hepatic neutral lipid flux. Clustering of chemical-genetic interactions identified CLIC-like chloride channel 1 (CLCC1) as a critical regulator of neutral lipid storage and secretion. Loss of CLCC1 resulted in the buildup of large LDs in hepatoma cells and knockout in mice caused liver steatosis. Remarkably, the LDs are in the lumen of the ER and exhibit properties of lipoproteins, indicating a profound shift in neutral lipid flux. Finally, remote homology searches identified a domain in CLCC1 that is homologous to yeast Brl1p and Brr6p, factors that promote the fusion of the inner and outer nuclear envelopes during nuclear pore complex assembly. Loss of CLCC1 lead to extensive nuclear membrane herniations, consistent with impaired nuclear pore complex assembly. Thus, we identify CLCC1 as the human Brl1p/Brr6p homolog and propose that CLCC1-mediated membrane remodeling promotes hepatic neutral lipid flux and nuclear pore complex assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS J.A.O. is a member of the scientific advisory board for Vicinitas Therapeutics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Female-age-dependent changes in the lipid fingerprint of the mammalian oocytes.Hum Reprod. 2024 Dec 1;39(12):2754-2767. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae225. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 39366679 Free PMC article.
-
Lesion-remote astrocytes govern microglia-mediated white matter repair.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 17:2024.03.15.585251. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.15.585251. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38558977 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7. PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Staging of Hepatic Fibrosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:539-574. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287864 Review.
References
-
- Dierge E. et al. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the acidic tumor environment leads to ferroptosis-mediated anticancer effects. Cell Metab 33, 1701–1715.e5 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
