Recent Advances in Amphipathic Peptidomimetics as Antimicrobial Agents to Combat Drug Resistance
- PMID: 38893366
- PMCID: PMC11173824
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112492
Recent Advances in Amphipathic Peptidomimetics as Antimicrobial Agents to Combat Drug Resistance
Abstract
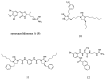
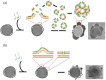
The development of antimicrobial drugs with novel structures and clear mechanisms of action that are active against drug-resistant bacteria has become an urgent need of safeguarding human health due to the rise of bacterial drug resistance. The discovery of AMPs and the development of amphipathic peptidomimetics have lay the foundation for novel antimicrobial agents to combat drug resistance due to their overall strong antimicrobial activities and unique membrane-active mechanisms. To break the limitation of AMPs, researchers have invested in great endeavors through various approaches in the past years. This review summarized the recent advances including the development of antibacterial small molecule peptidomimetics and peptide-mimic cationic oligomers/polymers, as well as mechanism-of-action studies. As this exciting interdisciplinary field is continuously expanding and growing, we hope this review will benefit researchers in the rational design of novel antimicrobial peptidomimetics in the future.
Keywords: antimicrobial agents; drug resistance; peptidomimetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
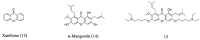

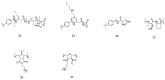
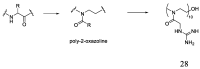
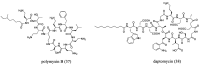
Similar articles
-
Development of novel membrane active lipidated peptidomimetics active against drug resistant clinical isolates.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Sep 1;22(17):4544-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.07.041. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25131957
-
Recent development of small antimicrobial peptidomimetics.Future Med Chem. 2012 Sep;4(14):1853-62. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.111. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23043481 Review.
-
Antimicrobial AApeptides.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(11):1266-1279. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666161018145945. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27758686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of antimicrobial peptides against microbial biofilms: advantages and limits.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(2):256-79. doi: 10.2174/092986711794088399. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21110801 Review.
-
Advances in Development of Antimicrobial Peptidomimetics as Potential Drugs.Molecules. 2017 Aug 29;22(9):1430. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091430. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28850098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Biomedical Applications: A Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;13(9):794. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090794. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saiman L. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. JAMA. 2012;307:1865–1866. doi: 10.1001/jama.307.17.1865. - DOI
-
- Bee G.C.W., Lokken-Toyli K.L., Yeung S.T., Rodriguez L., Zangari T., Anderson E.E., Ghosh S., Rothlin C.V., Brodin P., Khanna K.M., et al. Age-dependent differences in efferocytosis determine the outcome of opsonophagocytic protection from invasive pathogens. Immunity. 2023;56:1255–1268. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.03.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

