Musculoskeletal Diseases as the Most Prevalent Component of Multimorbidity: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 38892800
- PMCID: PMC11172850
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113089
Musculoskeletal Diseases as the Most Prevalent Component of Multimorbidity: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
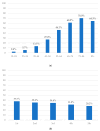
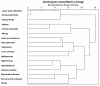
Background/Objectives: Due to their high frequency, common risk factors, and similar pathogenic mechanisms, musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are more likely to occur with other chronic illnesses, making them a "component disorder" of multimorbidity. Our objective was to assess the prevalence of multimorbidity and to identify the most common clusters of diagnosis within multimorbidity states, with the primary hypothesis that the most common clusters of multimorbidity are MSDs. Methods: The current study employed data from a population-based 2019 European Health Interview Survey (EHIS). Multimorbidity was defined as a ≥2 diagnosis from the list of 17 chronic non-communicable diseases, and to define clusters, the statistical method of hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) was performed. Results: Out of 13,178 respondents, multimorbidity was present among 4398 (33.4%). The HCA method yielded six multimorbidity clusters representing the most common diagnoses. The primary multimorbidity cluster, which was prevalent among both genders, age groups, incomes per capita, and statistical regions, consisted of three diagnoses: (1) lower spine deformity or other chronic back problem (back pain), (2) cervical deformity or other chronic problem with the cervical spine, and (3) osteoarthritis. Conclusions: Given the influence of musculoskeletal disorders on multimorbidity, it is imperative to implement appropriate measures to assist patients in relieving the physical discomfort and pain they endure. Public health information, programs, and campaigns should be utilized to promote a healthy lifestyle. Policymakers should prioritize the prevention of MSDs by encouraging increased physical activity and a healthy diet, as well as focusing on improving functional abilities.
Keywords: cervical deformity; hierarchical cluster analysis; low back deformity; multimorbidity; musculoskeletal disorders; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CHRONIC MULTIMORBIDITY OF LOW BACK PAIN OR OTHER CHRONIC BACK DISORDERS IN THE REPUBLIC OF CROATIA.Acta Clin Croat. 2023 Apr;62(1):141-152. doi: 10.20471/acc.2023.62.01.17. Acta Clin Croat. 2023. PMID: 38304360 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Multimorbidity Patterns in Elderly Primary Health Care Patients in a South Mediterranean European Region: A Cluster Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 2;10(11):e0141155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141155. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26524599 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of musculoskeletal disorders in multimorbidity: Implications for practice and policy.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Apr;31(2):129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 29224692 Review.
-
Trends, patterns and health consequences of multimorbidity among South Korea adults: Analysis of nationally representative survey data 2007-2016.J Glob Health. 2020 Dec;10(2):020426. doi: 10.7189/jogh.10.020426. J Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 33274065 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Academy of Medical Sciences. Multimorbidity: A Priority for Global Health Research. Academy of Medical Sciences. 2018. [(accessed on 15 April 2024)]. Available online: https://acmedsci.ac.uk/filedownload/82222577.
-
- Vadrevu L., Kumar V., Kanjilal B. Rising challenge of multiple morbidities among the rural poor in India—A case of the Sundarbans in West Bengal. Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health. 2016;5:343. doi: 10.5455/ijmsph.2016.25082015129. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

