From Environment to Gene Expression: Epigenetic Methylations and One-Carbon Metabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 38891099
- PMCID: PMC11171807
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110967
From Environment to Gene Expression: Epigenetic Methylations and One-Carbon Metabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
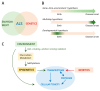
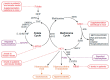
The etiology of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is complex and considered multifactorial. The majority of ALS cases are sporadic, but familial cases also exist. Estimates of heritability range from 8% to 61%, indicating that additional factors beyond genetics likely contribute to ALS. Numerous environmental factors are considered, which may add up and synergize throughout an individual's lifetime building its unique exposome. One level of integration between genetic and environmental factors is epigenetics, which results in alterations in gene expression without modification of the genome sequence. Methylation reactions, targeting DNA or histones, represent a large proportion of epigenetic regulations and strongly depend on the availability of methyl donors provided by the ubiquitous one-carbon (1C) metabolism. Thus, understanding the interplay between exposome, 1C metabolism, and epigenetic modifications will likely contribute to elucidating the mechanisms underlying altered gene expression related to ALS and to developing targeted therapeutic interventions. Here, we review evidence for 1C metabolism alterations and epigenetic methylation dysregulations in ALS, with a focus on the impairments reported in neural tissues, and discuss these environmentally driven mechanisms as the consequences of cumulative exposome or late environmental hits, but also as the possible result of early developmental defects.
Keywords: DNA methylation; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; epigenetics; histone methylation; one-carbon metabolism; therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The epigenetic approach of varicocele: a focus on sperm DNA and m6A-RNA methylation.Hum Reprod Update. 2024 Dec 13:dmae034. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmae034. Online ahead of print. Hum Reprod Update. 2024. PMID: 39673728
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative, physical and surgical interventions for managing faecal incontinence and constipation in adults with central neurological diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 29;10(10):CD002115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002115.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39470206
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

