Reprogramming Glioblastoma Cells into Non-Cancerous Neuronal Cells as a Novel Anti-Cancer Strategy
- PMID: 38891029
- PMCID: PMC11171681
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110897
Reprogramming Glioblastoma Cells into Non-Cancerous Neuronal Cells as a Novel Anti-Cancer Strategy
Abstract
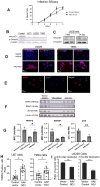
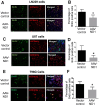
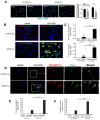
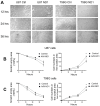
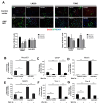
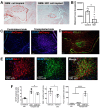
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive brain tumor with a high mortality rate. Direct reprogramming of glial cells to different cell lineages, such as induced neural stem cells (iNSCs) and induced neurons (iNeurons), provides genetic tools to manipulate a cell's fate as a potential therapy for neurological diseases. NeuroD1 (ND1) is a master transcriptional factor for neurogenesis and it promotes neuronal differentiation. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that the expression of ND1 in GBM cells can force them to differentiate toward post-mitotic neurons and halt GBM tumor progression. In cultured human GBM cell lines, including LN229, U87, and U373 as temozolomide (TMZ)-sensitive and T98G as TMZ-resistant cells, the neuronal lineage conversion was induced by an adeno-associated virus (AAV) package carrying ND1. Twenty-one days after AAV-ND1 transduction, ND1-expressing cells displayed neuronal markers MAP2, TUJ1, and NeuN. The ND1-induced transdifferentiation was regulated by Wnt signaling and markedly enhanced under a hypoxic condition (2% O2 vs. 21% O2). ND1-expressing GBM cultures had fewer BrdU-positive proliferating cells compared to vector control cultures. Increased cell death was visualized by TUNEL staining, and reduced migrative activity was demonstrated in the wound-healing test after ND1 reprogramming in both TMZ-sensitive and -resistant GBM cells. In a striking contrast to cancer cells, converted cells expressed the anti-tumor gene p53. In an orthotopical GBM mouse model, AAV-ND1-reprogrammed U373 cells were transplanted into the fornix of the cyclosporine-immunocompromised C57BL/6 mouse brain. Compared to control GBM cell-formed tumors, cells from ND1-reprogrammed cultures formed smaller tumors and expressed neuronal markers such as TUJ1 in the brain. Thus, reprogramming using a single-factor ND1 overcame drug resistance, converting malignant cells of heterogeneous GBM cells to normal neuron-like cells in vitro and in vivo. These novel observations warrant further research using patient-derived GBM cells and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models as a potentially effective treatment for a deadly brain cancer and likely other astrocytoma tumors.
Keywords: Wnt-3α; apoptosis; direct reprogramming; glioblastoma; hypoxia; induced neurons; p53; tumor growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3 reverses temozolomide resistance and restrains epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in glioblastoma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jan;110(1):389-400. doi: 10.1111/cas.13881. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30431207 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor I A promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via activation of nuclear factor κB pathway.Life Sci. 2019 Nov 1;236:116917. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116917. Epub 2019 Oct 12. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31614149
-
Modulating lncRNA SNHG15/CDK6/miR-627 circuit by palbociclib, overcomes temozolomide resistance and reduces M2-polarization of glioma associated microglia in glioblastoma multiforme.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 28;38(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1371-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31462285 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of Pathways and Therapeutic Targets.Cells. 2024 Sep 19;13(18):1574. doi: 10.3390/cells13181574. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical and clinical advances to overcome hypoxia in glioblastoma multiforme.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 13;15(7):503. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06904-2. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39003252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon-supported magnetic nanocomposite (MNPs-OLAC) obtained from okra leaves as a nanocarrier for targeted delivery of morin hydrate.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1482130. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1482130. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39444608 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

