Improvement of Theaflavins on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 38890991
- PMCID: PMC11171799
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111763
Improvement of Theaflavins on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
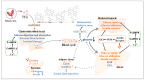
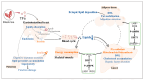
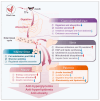
In diabetes mellitus, disordered glucose and lipid metabolisms precipitate diverse complications, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, contributing to a rising global mortality rate. Theaflavins (TFs) can improve disorders of glycolipid metabolism in diabetic patients and reduce various types of damage, including glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, and other associated secondary adverse effects. TFs exert effects to lower blood glucose and lipids levels, partly by regulating digestive enzyme activities, activation of OATP-MCT pathway and increasing secretion of incretins such as GIP. By the Ca2+-CaMKK ꞵ-AMPK and PI3K-AKT pathway, TFs promote glucose utilization and inhibit endogenous glucose production. Along with the regulation of energy metabolism by AMPK-SIRT1 pathway, TFs enhance fatty acids oxidation and reduce de novo lipogenesis. As such, the administration of TFs holds significant promise for both the prevention and amelioration of diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: black tea; dietary polyphenols; hyperglycemia; hypertriglyceridemia; insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoglycemic and lipid lowering effects of theaflavins in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Food Funct. 2021 Oct 19;12(20):9922-9931. doi: 10.1039/d1fo01966j. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34492673
-
The Effect of Theaflavins on the Gut Microbiome and Metabolites in Diabetic Mice.Foods. 2023 Oct 22;12(20):3865. doi: 10.3390/foods12203865. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37893758 Free PMC article.
-
Theaflavins Improve Insulin Sensitivity through Regulating Mitochondrial Biosynthesis in Palmitic Acid-Induced HepG2 Cells.Molecules. 2018 Dec 19;23(12):3382. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123382. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30572687 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiobesity Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Theaflavins.J Med Food. 2024 Jan;27(1):1-11. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2023.K.0180. Epub 2023 Dec 7. J Med Food. 2024. PMID: 38060708 Review.
-
Dietary plant flavonoids in prevention of obesity and diabetes.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;120:159-235. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32085882 Review.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

