Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with meteorological factors: a time series study in Hefei, China, and a literature review
- PMID: 38886269
- PMCID: PMC11222232
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-024-33943-1
Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with meteorological factors: a time series study in Hefei, China, and a literature review
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with meteorological factors: a time series study in Hefei, China, and a literature review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jul;31(35):48811. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34299-2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38972949 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
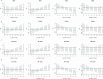
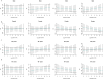
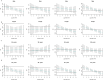
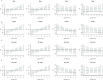
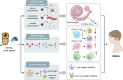
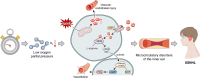
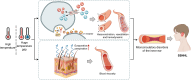
Air pollution can cause disease and has become a major global environmental problem. It is currently believed that air pollution may be related to the progression of SSNHL. As a rapidly developing city in recent years, Hefei has serious air pollution. In order to explore the correlation between meteorological variables and SSNHL admissions, we conducted this study. This study investigated the short-term associations between SSNHL patients admitted to the hospital and Hefei climatic variables. The daily data on SSNHL-related hospital admissions and meteorological variables containing mean temperature (T-mean; °C), diurnal temperature range (DTR; °C), atmospheric pressure (AP; Hp), and relative humidity (RH; %), from 2014 to 2021 (2558 days), were collected. A time-series analysis integrating distributed lag non-linear models and generalized linear models was used. PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched. Literature published up to August 2023 was reviewed to explore the potential impact mechanisms of meteorological factors on SSNHL. The mechanisms were determined in detail, focusing on wind speed, air pressure, temperature, humidity, and air pollutants. Using a median of 50.00% as a baseline, the effect of exceedingly low T-mean in the single-day hysteresis effect model began at a lag of 8 days (RR = 1.032, 95% CI: 1.001 ~ 1.064). High DTR affected the admission rate for SSNHL on lag 0 day. The significance of the effect was the greatest on that day (RR = 1.054, 95% CI: 1.007 ~ 1.104) and then gradually decreased. High and exceedingly high RH affected the admission rate SSNHL on lag 0 day, and these effects lasted for 8 and 7 days, respectively. There were significant associations between all grades of AP and SSNHL. This is the first study to assess the effect of meteorological variables on SSNHL-related admissions in China using a time-series approach. Long-term exposures to high DTR, RH values, low T-mean values, and all AP grades enhance the incidence of SSNHL in residents. Limiting exposure to extremes of ambient temperature and humidity may reduce the number of SSNHL-related hospital visits in the region. It is advisable to maintain a suitable living environment temperature and avoid extreme temperature fluctuations and high humidity. During periods of high air pollution, it is recommended to stay indoors and refrain from outdoor exercise.
Keywords: Air pollutants; Climatic variables; Mechanism; Outpatient; Sudden sensorineural hearing loss; Time-series analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of meteorological factor and air pollution on sudden sensorineural hearing loss using the health claims data in Busan, Republic of Korea.Am J Otolaryngol. 2019 May-Jun;40(3):393-399. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Am J Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30956004
-
Short-term effect of meteorological factors on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis hospital admissions: A distributed lag non-linear analysis in Hefei, China.Environ Res. 2022 May 1;207:112168. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112168. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 34655606
-
Long-term air pollution levels modify the relationships between short-term exposure to meteorological factors, air pollution and the incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease in children: a DLNM-based multicity time series study in Sichuan Province, China.BMC Public Health. 2022 Aug 4;22(1):1484. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13890-7. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35927638 Free PMC article.
-
Association between air pollution and sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL): A systematic review and meta-analysis.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 15;239(Pt 2):117392. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117392. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37838197 Review.
-
A Systematic Review on Heritability of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Laryngoscope. 2024 Aug;134(8):3447-3457. doi: 10.1002/lary.31308. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Laryngoscope. 2024. PMID: 38270208 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

