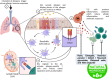
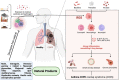
Revealing the mechanism and efficacy of natural products on treating the asthma: Current insights from traditional medicine to modern drug discovery
- PMID: 38882318
- PMCID: PMC11176852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32008
Revealing the mechanism and efficacy of natural products on treating the asthma: Current insights from traditional medicine to modern drug discovery
Abstract
Asthma remains a significant global health challenge, demanding innovative approaches to treatment. Traditional medicine has a rich history of using natural products to alleviate asthmatic symptoms. However, transitioning from these traditional remedies to modern drug discovery approaches has provided fresh insights into the mechanisms and effectiveness of these natural products. This study provides our comprehensive review, which examines the current state of knowledge in the treatment of asthma. It delves into the mechanisms through which natural products ameliorate asthma symptoms, and it discusses their potential in the development of novel therapeutic interventions. Our analysis reveals that natural products, traditionally employed for asthma relief, exhibit diverse mechanisms of action. These include anti-inflammatory, bronchodilatory, immunomodulatory effects, and reducing gene expression. In the context of modern drug discovery, these natural compounds serve as valuable candidates for the development of novel asthma therapies. The transition from traditional remedies to modern drug discovery represents a promising avenue for asthma treatment. Our review highlights the substantial efficacy of natural products in managing asthma symptoms, underpinned by well-defined mechanisms of action. By bridging the gap between traditional and contemporary approaches, we contribute to the growing body of knowledge in the field, emphasizing the potential of natural products in shaping the future of asthma therapy.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Asthma; Efficacy; Herbal medicines; Immunomodulatory; Modern drug; Natural product; Traditional medicine.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and mechanisms of action of traditional Chinese medicines for treating asthma and allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Feb;123(2):297-306; quiz 307-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.12.026. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19203653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural product-derived therapies for treating drug-resistant epilepsies: From ethnopharmacology to evidence-based medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116740. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116740. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37315641 Review.
-
Discovery of potential asthma targets based on the clinical efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine formulas.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 24;252:112635. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112635. Epub 2020 Jan 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32004629
-
Treatment of asthma and food allergy with herbal interventions from traditional chinese medicine.Mt Sinai J Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;78(5):697-716. doi: 10.1002/msj.20294. Mt Sinai J Med. 2011. PMID: 21913200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Medicinal Plants Conferring Protection Against Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma in Experimental Animals: A Review.J Asthma Allergy. 2021 Jun 14;14:641-662. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S296391. eCollection 2021. J Asthma Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34163178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Asthma. 2023 https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous