This is a preprint.
Efficient small fragment sequencing of human, cow, and bison miRNA, small RNA or csRNA-seq libraries using AVITI
- PMID: 38854037
- PMCID: PMC11160585
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596343
Efficient small fragment sequencing of human, cow, and bison miRNA, small RNA or csRNA-seq libraries using AVITI
Update in
-
Efficient small fragment sequencing of human, cattle, and bison miRNA, small RNA, or csRNA-seq libraries using AVITI.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 29;25(1):1157. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11013-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39614157 Free PMC article.
Abstract
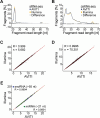
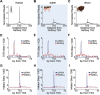
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) catalyzed breakthroughs across various scientific domains. Illumina's sequencing by synthesis method has long been essential for NGS but emerging technologies like Element Biosciences' sequencing by avidity (AVITI) represent a novel approach. It has been reported that AVITI offers improved signal-to-noise ratios and cost reductions. However, the method relies on rolling circle amplification which can be impacted by polymer size, raising questions about its efficacy sequencing small RNAs (sRNA) molecules including microRNAs (miRNAs), piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), and others that are crucial regulators of gene expression and involved in various biological processes. In addition, capturing capped small RNAs (csRNA-seq) has emerged as a powerful method to map active or "nascent" RNA polymerase II transcription initiation in tissues and clinical samples. Here, we report a new protocol for seamlessly sequencing short DNA fragments on the AVITI and demonstrate that AVITI and Illumina sequencing technologies equivalently capture human, cattle (Bos taurus) and the bison (Bison bison) sRNA or csRNA sequencing libraries, augmenting the confidence in both approaches. Additionally, analysis of generated nascent transcription start sites (TSSs) data for cattle and bison revealed inaccuracies in their current genome annotations and highlighted the possibility and need to translate small RNA sequencing methodologies to livestock. Our accelerated and optimized protocol therefore bridges the advantages of AVITI sequencing and critical methods that rely on sequencing short DNA fragments.
Keywords: AVITI; Illumina; capped small RNA sequencing (csRNA-seq); livestock; small RNA sequencing (sRNA-seq).
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS A.M.B, X.Q., and J.Z are employees of Element Biosciences. S.H.D. is leading nascent Transcriptomic Services (nTSS) at Washington State University.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient small fragment sequencing of human, cattle, and bison miRNA, small RNA, or csRNA-seq libraries using AVITI.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 29;25(1):1157. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11013-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39614157 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7 PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
References
-
- Ceasar SA, Rajan V, Prykhozhij SV, Berman JN, Ignacimuthu S. 2016. Insert, remove or replace: A highly advanced genome editing system using CRISPR/Cas9. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1863: 2333–2344. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
