Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in primary sensory neurons are implicated in CB2 agonist-mediated suppression of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic nociception and sexually-dimorphic sparing of morphine tolerance
- PMID: 38850666
- PMCID: PMC11209786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116879
Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in primary sensory neurons are implicated in CB2 agonist-mediated suppression of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic nociception and sexually-dimorphic sparing of morphine tolerance
Abstract
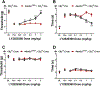
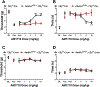
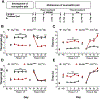
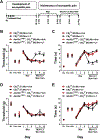
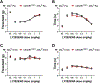
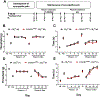
Cannabinoid CB2 agonists show therapeutic efficacy without unwanted CB1-mediated side effects. The G protein-biased CB2 receptor agonist LY2828360 attenuates the maintenance of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic nociception in male mice and blocks development of morphine tolerance in this model. However, the cell types involved in this phenomenon are unknown and whether this therapeutic profile is observed in female mice has never been investigated. We used conditional deletion of CB2 receptors to determine the cell population(s) mediating the anti-allodynic and morphine-sparing effects of CB2 agonists. Anti-allodynic effects of structurally distinct CB2 agonists (LY2828360 and AM1710) were present in paclitaxel-treated CB2f/f mice and in mice lacking CB2 receptors in CX3CR1 expressing microglia/macrophages (CX3CR1CRE/+; CB2f/f), but were absent in mice lacking CB2 receptors in peripheral sensory neurons (AdvillinCRE/+; CB2f/f). The morphine-sparing effect of LY28282360 occurred in a sexually-dimorphic manner, being present in male, but not female, mice. LY2828360 treatment (3 mg/kg per day i.p. x 12 days) blocked the development of morphine tolerance in male CB2f/f and CX3CR1CRE/+; CB2f/f mice with established paclitaxel-induced neuropathy but was absent in male (or female) AdvillinCRE/+; CB2f/f mice. Co-administration of morphine with a low dose of LY2828360 (0.1 mg/kg per day i.p. x 6 days) reversed morphine tolerance in paclitaxel-treated male CB2f/f mice, but not AdvillinCRE/+; CB2f/f mice of either sex. LY2828360 (3 mg/kg per day i.p. x 8 days) delayed, but did not prevent, the development of paclitaxel-induced mechanical or cold allodynia in either CB2f/f or CX3CR1CRE/+; CB2f/f mice of either sex. Our findings have potential clinical implications.
Keywords: CB2; Cancer; Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; Dorsal root ganglion; Opioid tolerance.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no financial/personal interest or belief that could affect the objectivity of this manuscript. Dr. Hohmann is a consultant for Anagin Inc.
Figures
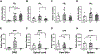
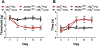

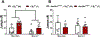

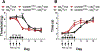
Update of
-
Cannabinoid CB 2 receptors in primary sensory neurons are implicated in CB 2 agonist-mediated suppression of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic nociception and sexually-dimorphic sparing of morphine tolerance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 10:2024.03.05.583426. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583426. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116879. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116879 PMID: 38496640 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid CB 2 receptors in primary sensory neurons are implicated in CB 2 agonist-mediated suppression of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic nociception and sexually-dimorphic sparing of morphine tolerance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 10:2024.03.05.583426. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583426. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116879. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116879 PMID: 38496640 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist LY2828360 synergizes with morphine to suppress neuropathic nociception and attenuates morphine reward and physical dependence.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 5;886:173544. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173544. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32896549 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral sensory neuron CB2 cannabinoid receptors are necessary for both CB2-mediated antinociceptive efficacy and sparing of morphine tolerance in a mouse model of anti-retroviral toxic neuropathy.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Jan;187:106560. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106560. Epub 2022 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36417942 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating the endocannabinoid pathway as treatment for peripheral neuropathic pain: a selected review of preclinical studies.Ann Palliat Med. 2017 Dec;6(Suppl 2):S209-S214. doi: 10.21037/apm.2017.08.04. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Ann Palliat Med. 2017. PMID: 29156899 Review.
-
The effect of cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist on morphine tolerance.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023 Dec 1;16:43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.11.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38145173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Recent Update on Pathophysiology and Treatment.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;14(8):991. doi: 10.3390/life14080991. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Habibi-Asl B, Vaez H, Najafi M, Bidaghi A, Ghanbarzadeh S, Attenuation of morphine-induced dependence and tolerance by ceftriaxone and amitriptyline in mice, Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwan 52 (2014) 163–168. - PubMed
-
- Mansouri MT, Khodayar MJ, Tabatabaee A, Ghorbanzadeh B, Naghizadeh B, Modulation of morphine antinociceptive tolerance and physical dependence by co-administration of simvastatin, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav 137 (2015) 38–43. - PubMed
-
- Hassanipour M, Amini-Khoei H, Shafaroodi H, Shirzadian A, Rahimi N, Imran-Khan M, Rezayat SM, Dehpour A, Atorvastatin attenuates the antinociceptive tolerance of morphine via nitric oxide dependent pathway in male mice, Brain. Res. Bull 125 (2016) 173–180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

