IRF8 maintains mononuclear phagocyte and neutrophil function in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 38845872
- PMCID: PMC11153194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31818
IRF8 maintains mononuclear phagocyte and neutrophil function in acute kidney injury
Abstract
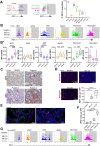
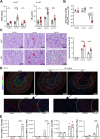
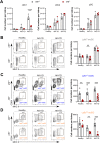
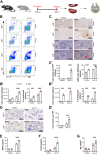
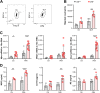
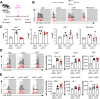
Immune cells are key players in acute tissue injury and inflammation, including acute kidney injury (AKI). Their development, differentiation, activation status, and functions are mediated by a variety of transcription factors, such as interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) and IRF4. We speculated that IRF8 has a pathophysiologic impact on renal immune cells in AKI and found that IRF8 is highly expressed in blood type 1 conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s), monocytes, monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDCs) and kidney biopsies from patients with AKI. In a mouse model of ischemia‒reperfusion injury (IRI)-induced AKI, Irf8 -/- mice displayed increased tubular cell necrosis and worsened kidney dysfunction associated with the recruitment of a substantial amount of monocytes and neutrophils but defective renal infiltration of cDC1s and moDCs. Mechanistically, global Irf8 deficiency impaired moDC and cDC1 maturation and activation, as well as cDC1 proliferation, antigen uptake, and trafficking to lymphoid organs for T-cell priming in ischemic AKI. Moreover, compared with Irf8 +/+ mice, Irf8 -/- mice exhibited increased neutrophil recruitment and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation following AKI. IRF8 primarily regulates cDC1 and indirectly neutrophil functions, and thereby protects mice from kidney injury and inflammation following IRI. Our results demonstrate that IRF8 plays a predominant immunoregulatory role in cDC1 function and therefore represents a potential therapeutic target in AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Dendritic cell; Inflammation; Interferon regulatory factor 8; Monocyte; Neutrophil.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IRF8-Dependent Type I Conventional Dendritic Cells (cDC1s) Control Post-Ischemic Inflammation and Mildly Protect Against Post-Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury and Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 21;12:685559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685559. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34234783 Free PMC article.
-
IRF8 Transcription Factor Controls Survival and Function of Terminally Differentiated Conventional and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, Respectively.Immunity. 2016 Sep 20;45(3):626-640. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.08.013. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27637148
-
IRF4 and IRF8 Act in CD11c+ Cells To Regulate Terminal Differentiation of Lung Tissue Dendritic Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Feb 15;196(4):1666-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501870. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26746189 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 8 and the regulation of neutrophil, monocyte, and dendritic cell production.Curr Opin Hematol. 2016 Jan;23(1):11-7. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000196. Curr Opin Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26554887 Review.
-
Regulation of myelopoiesis by the transcription factor IRF8.Int J Hematol. 2015 Apr;101(4):342-51. doi: 10.1007/s12185-015-1761-9. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Int J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25749660 Review.
References
-
- Sharfuddin A.A., Molitoris B.A. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:189–200. - PubMed
-
- Dong X., Swaminathan S., Bachman L.A., Croatt A.J., Nath K.A., Griffin M.D. Resident dendritic cells are the predominant TNF-secreting cell in early renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2007;71:619–628. - PubMed
-
- Kurts C., Ginhoux F., Panzer U. Kidney dendritic cells: fundamental biology and functional roles in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020;16:391–407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

