Investigation of miltefosine-model membranes interactions at the molecular level for two different PS levels modeling cancer cells
- PMID: 38833041
- PMCID: PMC11217121
- DOI: 10.1007/s10863-024-10025-y
Investigation of miltefosine-model membranes interactions at the molecular level for two different PS levels modeling cancer cells
Abstract
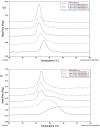
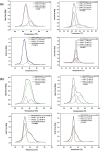
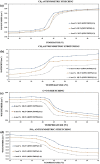
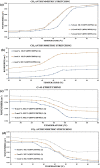
Miltefosine (MLT) is a broad-spectrum drug included in the alkylphospholipids (APL) used against leishmania and various types of cancer. The most crucial feature of APLs is that they are thought to only kill cancerous cells without harming normal cells. However, the molecular mechanism of action of APLs is not completely understood. The increase in the phosphatidylserine (PS) ratio is a marker showing the stage of cancer and even metastasis. The goal of this research was to investigate the molecular effects of miltefosine at the molecular level in different PS ratios. The effects of MLT on membrane phase transition, membrane orders, and dynamics were studied using DPPC/DPPS (3:1) and DPPC/DPPS (1:1) multilayer (MLV) vesicles mimicking DPPS ratio variation, Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), and Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Our findings indicate that miltefosine is evidence at the molecular level that it is directed towards the tumor cell and that the drug's effect increases with the increase of anionic lipids in the membrane depending on the stage of cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; Differential scanning calorimetry; Dipalmitoyl phosphatidylserine level; Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy; Miltefosine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of miltefosine with intercellular membranes of stratum corneum and biomimetic lipid vesicles.Int J Pharm. 2012 Sep 15;434(1-2):391-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Int J Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22692081
-
Alterations in the homeostasis of phospholipids and cholesterol by antitumor alkylphospholipids.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Mar 25;9:33. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-33. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20338039 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro effects of the antitumor drug miltefosine on human erythrocytes and molecular models of its membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Jan;1861(1):17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 30336115
-
Anticancer alkylphospholipids: mechanisms of action, cellular sensitivity and resistance, and clinical prospects.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(21):2061-74. doi: 10.2174/138161208785294636. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18691116 Review.
-
Unmasking the Mechanism behind Miltefosine: Revealing the Disruption of Intracellular Ca2+ Homeostasis as a Rational Therapeutic Target in Leishmaniasis and Chagas Disease.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 27;14(4):406. doi: 10.3390/biom14040406. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arrieta MRR, Canseco EU, Casas SP. Simultaneous encapsulation of hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules in liposomes of DSPC. Thermochimica Acta. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2019.178462. - DOI
-
- Canseco EU, Casas SP. Spherical and tubular dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:399–409. doi: 10.1007/s10973-019-08416-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

