Myeloid Targeted Human MLL-ENL and MLL-AF9 Induces cdk9 and bcl2 Expression in Zebrafish Embryos
- PMID: 38829886
- PMCID: PMC11175583
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011308
Myeloid Targeted Human MLL-ENL and MLL-AF9 Induces cdk9 and bcl2 Expression in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
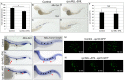
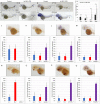
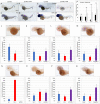
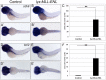
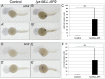
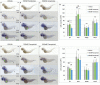
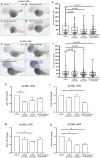
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) accounts for greater than twenty thousand new cases of leukemia annually in the United States. The average five-year survival rate is approximately 30%, pointing to the need for developing novel model systems for drug discovery. In particular, patients with chromosomal rearrangements in the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene have higher relapse rates with poor outcomes. In this study we investigated the expression of human MLL-ENL and MLL-AF9 in the myeloid lineage of zebrafish embryos. We observed an expansion of MLL positive cells and determined these cells colocalized with the myeloid markers spi1b, mpx, and mpeg. In addition, expression of MLL-ENL and MLL-AF9 induced the expression of endogenous bcl2 and cdk9, genes that are often dysregulated in MLL-r-AML. Co-treatment of lyz: MLL-ENL or lyz:MLL-AF9 expressing embryos with the BCL2 inhibitor, Venetoclax, and the CDK9 inhibitor, Flavopiridol, significantly reduced the number of MLL positive cells compared to embryos treated with vehicle or either drug alone. In addition, cotreatment with Venetoclax and Flavopiridol significantly reduced the expression of endogenous mcl1a compared to vehicle, consistent with AML. This new model of MLL-r-AML provides a novel tool to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying disease progression and a platform for drug discovery.
Copyright: © 2024 Belt et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The CDK9 Inhibitor Dinaciclib Exerts Potent Apoptotic and Antitumor Effects in Preclinical Models of MLL-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 1;76(5):1158-69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1070. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26627013
-
Impact of elevated anti-apoptotic MCL-1 and BCL-2 on the development and treatment of MLL-AF9 AML in mice.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jul;26(7):1316-1331. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0209-1. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30470795 Free PMC article.
-
MLL-AF9 regulates transcriptional initiation in mixed lineage leukemic cells.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107566. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107566. Epub 2024 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39002676 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from mouse models of MLL fusion gene-driven acute leukemia.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Aug;1863(8):194550. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194550. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32320749 Review.
-
The YEATS domain epigenetic reader proteins ENL and AF9 and their therapeutic value in leukemia.Exp Hematol. 2023 Aug;124:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2023.06.001. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Exp Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37295550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Developments and Evolving Therapeutic Strategies in KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Leukemia.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70326. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70326. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39428967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

