Unlocking the Medicinal Potential of Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: current Progress and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 38828203
- PMCID: PMC11141722
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S463145
Unlocking the Medicinal Potential of Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: current Progress and Future Perspectives
Abstract
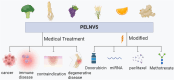
Botanical preparations for herbal medicine have received more and more attention from drug researchers, and the extraction of active ingredients and their successful clinical application have become an important direction of drug research in major pharmaceutical companies, but the complexity of extracts, multiple side effects, and significant individual differences have brought many difficulties to the clinical application of herbal preparations. It is noteworthy that extracellular vesicles as active biomolecules extracted from medicinal plants are believed to be useful for the treatment of a variety of diseases, including cancer, inflammation, regenerative-restorative and degenerative diseases, which may provide a new direction for the clinical utilization of herbal preparations. In this review, we sort out recent advances in medicinal plant extracellular vesicles and discuss their potential as disease therapeutics. Finally, future challenges and research directions for the clinical translation of medicinal plant extracellular vesicles are also discussed, and we expect that continued development based on medicinal plant extracellular vesicles will facilitate the clinical application of herbal preparations.
Keywords: Chinese medicine preparation; drug delivery nanoplatforms; nanoparticle; nanotherapeutics; plant-derived extracellular vesicles.
© 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[From medicinal plant to phytotherapeutic drug].Ther Umsch. 2002 Jun;59(6):275-82. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.59.6.275. Ther Umsch. 2002. PMID: 12125176 German.
-
Phytotherapy of Hypertension: An Updated Overview.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020;20(6):812-839. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666191227104648. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 31880255 Review.
-
Advancing therapeutic efficacy: nanovesicular delivery systems for medicinal plant-based therapeutics.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7229-7254. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03104-9. Epub 2024 May 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38700796 Review.
-
Medicinal plants in Brazil: Pharmacological studies, drug discovery, challenges and perspectives.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Oct;112:4-29. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.01.021. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 26812486 Review.
-
Medicinal plants for epileptic seizures: Phytoconstituents, pharmacology and mechanisms revisited.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Feb 10;320:117386. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117386. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37956914 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

