Directly targeting BAX for drug discovery: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges
- PMID: 38828138
- PMCID: PMC11143528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.010
Directly targeting BAX for drug discovery: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges
Abstract
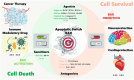
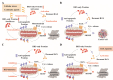
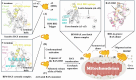
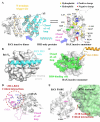
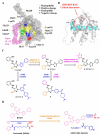
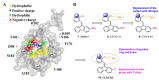
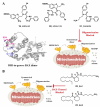
For over two decades, the development of B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family therapeutics has primarily focused on anti-apoptotic proteins, resulting in the first-in-class drugs called BH3 mimetics, especially for Bcl-2 inhibitor Venetoclax. The pro-apoptotic protein Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX) plays a crucial role as the executioner protein of the mitochondrial regulated cell death, contributing to organismal development, tissue homeostasis, and immunity. The dysregulation of BAX is closely associated with the onset and progression of diseases characterized by pathologic cell survival or death, such as cancer, neurodegeneration, and heart failure. In addition to conducting thorough investigations into the physiological modulation of BAX, research on the regulatory mechanisms of small molecules identified through biochemical screening approaches has prompted the identification of functional and potentially druggable binding sites on BAX, as well as diverse all-molecule BAX modulators. This review presents recent advancements in elucidating the physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX and in identifying potentially druggable binding sites on BAX. Furthermore, it highlights the structural and mechanistic insights into small-molecule modulators targeting diverse binding surfaces or conformations of BAX, offering a promising avenue for developing next-generation apoptosis modulators to treat a wide range of diseases associated with dysregulated cell death by directly targeting BAX.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Dynamic conformational activation; Pro-apoptotic protein BAX; Small-molecule apoptosis modulators.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Mar;43(3):206-220. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.11.001. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34848097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) homology domain 3 (BH3) mimetics demonstrate differential activities dependent upon the functional repertoire of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 19;289(38):26481-26491. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569632. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25096574 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphoma cells lacking pro-apoptotic BAX are highly resistant to BH3-mimetics targeting pro-survival MCL-1 but retain sensitivity to conventional DNA-damaging drugs.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Apr;30(4):1005-1017. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01117-0. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36755070 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting BAX to drug death directly.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Jul;15(7):657-665. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0306-6. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31209350 Review.
-
BH3 Mimetic Peptides: An Effective Strategy to Complement Anticancer Therapy.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023;24(10):853-864. doi: 10.2174/1389203724666230822100131. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023. PMID: 37608654 Review.
Cited by
-
Isoliquiritigenin alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction via activating the Nrf2 pathway.Redox Biol. 2024 Nov;77:103406. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103406. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39454290 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological research of new imidazolone-sulphonamide-pyrimidine hybrids as potential EGFR-TK inhibitors and apoptosis-inducing agents.RSC Adv. 2024 Jun 24;14(28):20120-20129. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03157a. eCollection 2024 Jun 18. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38915323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czabotar P.E., Lessene G., Strasser A., Adams J.M. Control of apoptosis by the Bcl-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:49–63. - PubMed
-
- Oltvai Z.N., Milliman C.L., Korsmeyer S.J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993;74:609–619. - PubMed
-
- Kiefer M.C., Brauer M.J., Powers V.C., Wu J.J., Umansky S.R., Tomei L.D., et al. Modulation of apoptosis by the widely distributed Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature. 1995;374:736–739. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y., Finger L.R., Yunis J., Nowell P.C., Croce C.M. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984;226:1097–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

