Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of FOXD1 in various cancers: a meta and bioinformation analysis
- PMID: 38827805
- PMCID: PMC11140636
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2023-0085
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of FOXD1 in various cancers: a meta and bioinformation analysis
Abstract
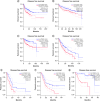
Aim: To examine both predictive and clinicopathological importance underlying FOXD1 in malignant tumors, our study adopts meta-analysis. Methods: We searched from PubMed, Embase, WOS, Wanfang and CNKI. Stata SE15.1 was used to calculate the risk ratio (HR) as well as relative risk (RR) with 95% of overall CIs to assess FOXD1 and overall survival rate (OS), disease-free survival rate as well as clinicopathological parameters. Results: 3808 individuals throughout 17 trials showed high FOXD1 expression was linked to disadvantaged OS (p < 0.001) and disease-free survival (p < 0.001) and higher TNM stage (p < 0.001). Conclusion: Elevated FOXD1 had worse predictions and clinicopathological parameters in most cancers. The GEPIA database findings also support our results.
Keywords: FOXD1; biomarkers; cancer; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Plain language summary
FOXD1 is a gene linked to a variety of cancers. In our article, we analyzed the results of several clinical trials in patients with different cancers. We found that when this gene is expressed in large amounts, it is often indicative of poor survival rates. From this study we can use FOXD1 to predict the course of the disease and at the same time study its upper and lower pathways to find therapeutic drugs to treat the cancer.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81860420), the Youth Foundation project of the Jiangxi provincial science and Technology Department (no. 20192BAB215031), and Jiangxi Province Department of Education (GJJ180141). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evidence from a meta-analysis for the prognostic and clinicopathological importance of DKC1 in malignancies.Future Oncol. 2023 Feb;19(6):473-484. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-1125. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Future Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36876511
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of kinesin family member C1 in various cancers: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(40):e17346. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017346. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31577729 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of FOXD1 and Plk2: A novel biomarker for predicting unfavourable prognosis of colorectal cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jun;26(12):3471-3482. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17361. Epub 2022 May 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35579380 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis of P4HB expression levels in the prognosis of cancer patients.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154474. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154474. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37119730 Review.
-
The prognosis and clinicopathological significance of histone deacetylase in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Sep;23(5):1515-1536. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00934-w. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36342581 Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72(1), 7–33 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Weigel D, Jürgens G, Küttner F, Seifert E, Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell 57(4), 645–658 (1989). - PubMed
-
• Shows us the history of how FOXD1 discovered.
-
- Lai E, Prezioso VR, Smith E, Litvin O, Costa RH, Darnell JE Jr. HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Develop. 4(8), 1427–1436 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Benayoun BA, Caburet S, Veitia RA. Forkhead transcription factors: key players in health and disease. Trends Genet. 27(6), 224–232 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

