Effect of prematurely elevated late follicular progesterone on pregnancy outcomes following ovarian stimulation-intrauterine insemination for unexplained infertility: secondary analysis of the AMIGOS trial
- PMID: 38822675
- PMCID: PMC11291944
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/deae113
Effect of prematurely elevated late follicular progesterone on pregnancy outcomes following ovarian stimulation-intrauterine insemination for unexplained infertility: secondary analysis of the AMIGOS trial
Abstract
Study question: What is the relationship between late follicular phase progesterone levels and clinic pregnancy and live birth rates in couples with unexplained infertility undergoing ovarian stimulation with IUI (OS-IUI)?
Summary answer: Late follicular progesterone levels between 1.0 and <1.5 ng/ml were associated with higher live birth and clinical pregnancy rates while the outcomes in groups with higher progesterone levels did not differ appreciably from the <1.0 ng/ml reference group.
What is known already: Elevated late follicular progesterone levels have been associated with lower live birth rates after fresh embryo transfer following controlled ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval, but less is known about whether an association exists with outcomes in OS-IUI cycles. Existing studies are few and have been limited to ovarian stimulation with gonadotrophins, but the use of oral agents, such as clomiphene citrate and letrozole, is common with these treatments and has not been well studied.
Study design, size, duration: The study was a prospective cohort analysis of the Assessment of Multiple Intrauterine Gestations from Ovarian Stimulation (AMIGOS) randomized controlled trial. Frozen serum was available for evaluation from 2121 cycles in 828 AMIGOS participants. The primary pregnancy outcome was live birth per cycle, and the secondary pregnancy outcome was clinical pregnancy rate per cycle.
Participants/materials, setting, methods: Couples with unexplained infertility in the AMIGOS trial, for whom female serum from day of trigger with hCG was available in at least one cycle of treatment, were included. Stored frozen serum samples from day of hCG trigger during treatment with OS-IUI were evaluated for serum progesterone level. Progesterone level <1.0 ng/ml was the reference group for comparison with progesterone categorized in increments of 0.5 ng/ml up to ≥3.0 ng/ml. Unadjusted and adjusted risk ratios (RR) and 95% CI were estimated using cluster-weighted generalized estimating equations to estimate modified Poisson regression models with robust standard errors.
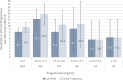
Main results and the role of chance: Compared to the reference group with 110/1363 live births (8.07%), live birth rates were significantly increased in cycles with progesterone 1.0 to <1.5 ng/ml (49/401 live births, 12.22%) in both the unadjusted (RR 1.56, 95% CI 1.14, 2.13) and treatment-adjusted models (RR 1.51, 95% CI 1.10, 2.06). Clinical pregnancy rates were also higher in this group (55/401 clinical pregnancies, 13.72%) compared to reference group with 130/1363 (9.54%) (unadjusted RR 1.46, 95% CI 1.10, 1.94 and adjusted RR 1.42, 95% CI 1.07, 1.89). In cycles with progesterone 1.5 ng/ml and above, there was no evidence of a difference in clinical pregnancy or live birth rates relative to the reference group. This pattern remained when stratified by ovarian stimulation treatment group but was only statistically significant in letrozole cycles.
Limitations, reasons for caution: The AMIGOS trial was not designed to answer this clinical question, and with small numbers in some progesterone categories our analyses were underpowered to detect differences between some groups. Inclusion of cycles with progesterone values above 3.0 ng/ml may have included those wherein ovulation had already occurred at the time the IUI was performed. These cycles would be expected to experience a lower success rate but pregnancy may have occurred with intercourse in the same cycle.
Wider implications of the findings: Compared to previous literature focusing primarily on OS-IUI cycles using gonadotrophins, these data include patients using oral agents and therefore may be generalizable to the wider population of infertility patients undergoing IUI treatments. Because live births were significantly higher when progesterone ranged from 1.0 to <1.5 ng/ml, further study is needed to clarify whether this progesterone range may truly represent a prognostic indicator in OS-IUI cycles.
Study funding/competing interest(s): Oklahoma Shared Clinical and Translational Resources (U54GM104938) National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS). AMIGOS was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: U10 HD077680, U10 HD39005, U10 HD38992, U10 HD27049, U10 HD38998, U10 HD055942, HD055944, U10 HD055936, and U10HD055925. Research made possible by the funding by American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. Dr Burks has disclosed that she is a member of the Board of Directors of the Pacific Coast Reproductive Society. Dr Hansen has disclosed that he is the recipient of NIH grants unrelated to the present work, and contracts with Ferring International Pharmascience Center US and with May Health unrelated to the present work, as well as consulting fees with May Health also unrelated to the present work. Dr Diamond has disclosed that he is a stockholder and a member of the Board of Directors of Advanced Reproductive Care, Inc., and that he has a patent pending for the administration of progesterone to trigger ovulation. Dr Anderson, Dr Gavrizi, and Dr Peck do not have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Trial registration number: N/A.
Keywords: IUI; infertility; intrauterine insemination; ovarian stimulation; progesterone; unexplained infertility.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Conflict of interest statement
H.R.B. has disclosed that she is a member of the Board of Directors of the Pacific Coast Reproductive Society. K.R.H has disclosed that he is the recipient of NIH grants unrelated to the present work, and contracts with Ferring International Pharmascience Center US and with May Health unrelated to the present work, as well as consulting fees with May Health also unrelated to the present work. M.P.D. has disclosed that he is a stockholder and a member of the Board of Directors of Advanced Reproductive Care, Inc., and that he has a patent pending for the administration of progesterone to trigger ovulation. Z.S.A., S.G., and J.D.P. do not have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrauterine insemination performance characteristics and post-processing total motile sperm count in relation to live birth for couples with unexplained infertility in a randomised, multicentre clinical trial.Hum Reprod. 2020 Jun 1;35(6):1296-1305. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa027. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32432326 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Allostatic load, a measure of chronic physiological stress, is associated with pregnancy outcomes, but not fertility, among women with unexplained infertility.Hum Reprod. 2018 Sep 1;33(9):1757-1766. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey261. Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 30085177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factors associated with study protocol adherence and bio banking participation in reproductive medicine clinical trials and their relationship to live birth.Hum Reprod. 2020 Dec 1;35(12):2819-2831. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa232. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 33190149 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro fertilisation for unexplained subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD003357. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003357.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Apr 18;(4):CD003357. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003357.pub3 PMID: 15846658 Updated. Review.
-
Intra-uterine insemination for unexplained subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 19;2:CD001838. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001838.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 3;3:CD001838. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001838.pub6 PMID: 26892070 Updated. Review.
References
-
- Andersen AG, Als-Nielsen B, Hornnes PJ, Franch Andersen L. Time interval from human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) injection to follicular rupture. Hum Reprod 1995;10:3202–3205. - PubMed
-
- Cantineau AE, Cohlen BJ, Dutch I; Dutch IUI Study Group. The prevalence and influence of luteinizing hormone surges in stimulated cycles combined with intrauterine insemination during a prospective cohort study. Fertil Steril 2007;88:107–112. - PubMed
-
- Cunha-Filho JS, Kadoch J, Righini C, Fanchin R, Frydman R, Olivennes F. Premature LH and progesterone rise in intrauterine insemination cycles: analysis of related factors. Reprod Biomed Online 2003;7:194–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

